Imports#
import sys
sys.path.insert(1, "./../")
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from pathlib import Path
from settings import config
from datetime import date
import warnings
from scipy.stats import norm, stats
from scipy import stats
from scipy.stats import shapiro, jarque_bera, normaltest, skew, kurtosis
import plotly.io as pio
pio.templates.default = "plotly_white"
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
OUTPUT_DIR = Path(config("OUTPUT_DIR"))
DATA_DIR = Path(config("DATA_DIR"))
WRDS_USERNAME = config("WRDS_USERNAME")
START_DATE_01 = date(1996, 1, 1)
END_DATE_01 = date(2012, 1, 31)
START_DATE_02 = date(2012, 2, 1)
END_DATE_02 = date(2024, 12, 31)
DATE_RANGE = f"{pd.Timestamp(START_DATE_01):%Y-%m}_{pd.Timestamp(END_DATE_02):%Y-%m}"
Functions#
# --- Black-Scholes elasticity ---
def bs_elasticity(S, K, T, r, sigma, option_type="call"):
d1 = (np.log(S / K) + (r + 0.5 * sigma**2) * T) / (sigma * np.sqrt(T))
if option_type == "call":
price = S * norm.cdf(d1) - K * np.exp(-r * T) * norm.cdf(
d1 - sigma * np.sqrt(T)
)
delta = norm.cdf(d1)
else:
price = K * np.exp(-r * T) * norm.cdf(-d1 + sigma * np.sqrt(T)) - S * norm.cdf(
-d1
)
delta = -norm.cdf(-d1)
return (delta * S / price), price
# Gaussian kernel function
def kernel_weights(m_grid, ttm_grid, k_s, ttm, bw_m=0.0125, bw_t=10):
m_grid = np.asarray(m_grid, dtype=float)
ttm_grid = np.asarray(ttm_grid, dtype=float)
x = (m_grid - k_s) / bw_m
y = (ttm_grid - ttm) / bw_t
dist_sq = x**2 + y**2
weights = np.exp(-0.5 * dist_sq)
return weights / weights.sum() if weights.sum() > 0 else np.zeros_like(weights)
# --- Construct a single day portfolio ---
def construct_portfolio(data, k_s_target, ttm_target, option_type="call", r=0.01):
subset = data[(data["option_type"] == option_type)]
weights = kernel_weights(subset["moneyness"], subset["ttm"], k_s_target, ttm_target)
subset = subset.assign(weight=weights)
subset = subset[subset["weight"] > 0.01]
subset["weight"] /= subset["weight"].sum()
# Leverage-adjusted returns
elast, price = bs_elasticity(
S=subset["underlying"],
K=subset["strike"],
T=subset["ttm"] / 365,
r=r,
sigma=subset["iv"],
option_type=option_type,
)
subset["leverage_return"] = subset["daily_return"] / elast
return (subset["leverage_return"] * subset["weight"]).sum()
# --- Main Loop (simplified) ---
def build_portfolios(option_data, m_grid, ttm_grid, option_types=["call", "put"]):
portfolios = []
for opt_type in option_types:
for k_s in m_grid:
for ttm in ttm_grid:
ret = construct_portfolio(option_data, k_s, ttm, option_type=opt_type)
portfolios.append(
{"type": opt_type, "moneyness": k_s, "ttm": ttm, "return": ret}
)
return pd.DataFrame(portfolios)
def calc_kernel_weights(spx_mod):
"""Calculate kernel weights for each option in the SPX dataset based on moneyness and maturity targets.
This function iterates through predefined moneyness and maturity targets, applies kernel weights to candidate options."""
# Define moneyness and maturity targets from the paper
moneyness_targets = [0.90, 0.925, 0.950, 0.975, 1.000, 1.025, 1.050, 1.075, 1.100]
maturity_targets = [30, 60, 90]
cp_flags = ["C", "P"]
# Preprocess base DataFrame
spx_mod["days_to_maturity_int"] = spx_mod["days_to_maturity"].dt.days
spx_mod = spx_mod.reset_index()
spx_mod["original_index"] = spx_mod.index
weight_results = []
# Iterate through each strategy target
for cp_flag in cp_flags:
for target_moneyness in moneyness_targets:
for target_ttm in maturity_targets:
# Filter candidate options
candidate_options = spx_mod[
(spx_mod["cp_flag"] == cp_flag)
& (spx_mod["moneyness_id"] == target_moneyness)
& (spx_mod["maturity_id"] == target_ttm)
].copy()
if candidate_options.empty:
continue
candidate_options["kernel_weight"] = np.nan
# Apply kernel weights per date
for date, g in candidate_options.groupby("date"):
idx = g.index
weights = kernel_weights(
g["moneyness"].values,
g["days_to_maturity_int"].values,
k_s=target_moneyness,
ttm=target_ttm,
)
candidate_options.loc[idx, "kernel_weight"] = weights
weight_results.append(
candidate_options[["original_index", "kernel_weight"]]
)
# Merge weights back into spx_mod
if weight_results:
all_weights = pd.concat(weight_results).set_index("original_index")
spx_mod.set_index("original_index", inplace=True)
spx_mod["kernel_weight"] = all_weights["kernel_weight"]
spx_mod.reset_index(inplace=True)
else:
print("No matching options found for any target.")
spx_mod.drop(columns=["original_index"], inplace=True)
return spx_mod
def calc_option_delta_elasticity(df):
df = df.copy()
T = df["days_to_maturity"].dt.days / 365.0
S = df["close"]
K = df["strike_price"]
r = df["tb_m3"] / 100
sigma = df["IV"]
d1 = (np.log(S / K) + (r + 0.5 * sigma**2) * T) / (sigma * np.sqrt(T))
df = df.assign(
option_delta=np.where(df["cp_flag"] == "C", norm.cdf(d1), norm.cdf(d1) - 1),
option_elasticity=lambda x: x["option_delta"] * x["close"] / x["mid_price"],
)
return df
def read_option_data(filename):
# Example string interval: '(0.9, 0.95]'
# Remove whitespace and parse the string into tuples
def parse_interval_string(s):
# Handle missing or malformed entries gracefully
if pd.isnull(s) or not isinstance(s, str):
return pd.NA # or np.nan
s = s.strip().replace("(", "").replace("]", "")
try:
left, right = map(float, s.split(","))
return pd.Interval(left, right, closed="right")
except ValueError:
return pd.NA
df = pd.read_parquet(filename)
# restore the 'moneyness_bin' column as intervals
df["moneyness_bin"] = df["moneyness_bin"].apply(parse_interval_string)
return df
def compute_cjs_return_leverage_investment(spx_mod):
df = spx_mod.copy()
df = df.sort_values(["ftfsa_id", "date"])
# Lag price
df["mid_price_lag"] = df.groupby("ftfsa_id")["mid_price"].shift(1)
# Return and daily risk-free rate
df["option_return"] = (df["mid_price"] - df["mid_price_lag"]) / df["mid_price_lag"]
df["daily_rf"] = df["tb_m3"] / 100 / 252
# Weighted dollar investment and return contribution
df["inv_weight"] = df["kernel_weight"] / df["option_elasticity"]
df["inv_return"] = df["inv_weight"] * df["option_return"]
# Group and aggregate
grouped = df.groupby(["date", "ftfsa_id"])
port = grouped.agg(
total_inv_weight=("inv_weight", "sum"),
total_inv_return=("inv_return", "sum"),
daily_rf=("daily_rf", "first"),
cp_flag=("cp_flag", "first"),
).reset_index()
# Apply CJS logic
def adjusted_return(row):
if row["cp_flag"] == "C":
return (
row["total_inv_return"]
+ (1 - row["total_inv_weight"]) * row["daily_rf"]
)
elif row["cp_flag"] == "P":
return (
-row["total_inv_return"]
+ (1 + row["total_inv_weight"]) * row["daily_rf"]
)
else:
return np.nan
port["portfolio_return"] = port.apply(adjusted_return, axis=1)
return port
# Function to compute normality metrics
def normality_summary(df):
summary = []
for col in df.columns:
series = df[col].dropna()
shapiro_p = shapiro(series)[1]
jb_stat, jb_p = jarque_bera(series)
normaltest_p = normaltest(series)[1]
skew_val = skew(series)
kurt_val = kurtosis(series, fisher=False)
summary.append(
{
"Series": col,
"Shapiro_p": shapiro_p,
"JarqueBera_p": jb_p,
"Normaltest_p": normaltest_p,
"Skewness": skew_val,
"Kurtosis": kurt_val,
}
)
return pd.DataFrame(summary)
Execution#
# read filtered data
source_file = Path(DATA_DIR / "options" / f"spx_filtered_final_{DATE_RANGE}.parquet")
spx_filtered = read_option_data(filename=source_file)
spx_filtered = spx_filtered.reset_index()
# create the moneyness ID from the moneyness_bin column, using the right edge of the interval
spx_filtered["moneyness_id"] = spx_filtered["moneyness_bin"].apply(
lambda x: x.right if pd.notnull(x) else np.nan
)
# drop any rows where moneyness_id is NaN
spx_filtered = spx_filtered.dropna(subset=["moneyness_id"])
spx_filtered
| date | exdate | moneyness | secid | open | close | cp_flag | IV | tb_m3 | volume | ... | days_to_maturity | pc_parity_int_rate | intrinsic | log_iv | fitted_iv | rel_distance_iv | moneyness_bin | stdev_iv_moneyness_bin | is_outlier_iv | moneyness_id | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 0.987534 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.082711 | 5.04 | 444.0 | ... | 16 days | 0.015898 | 7.70 | -2.492403 | -2.377298 | 4.841838 | (0.975, 1.0] | 3.516840 | False | 1.000 |
| 1 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 1.019913 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.097356 | 5.04 | 4022.0 | ... | 16 days | 0.015898 | 0.00 | -2.329381 | -2.285771 | 1.907866 | (1.0, 1.025] | 5.219336 | False | 1.025 |
| 2 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 1.028007 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.101756 | 5.04 | 1627.0 | ... | 16 days | 0.015898 | 0.00 | -2.285177 | -2.264082 | 0.931727 | (1.025, 1.05] | 4.396845 | False | 1.050 |
| 3 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 1.036102 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.100588 | 5.04 | 0.0 | ... | 16 days | 0.015898 | 0.00 | -2.296722 | -2.242870 | 2.401027 | (1.025, 1.05] | 4.396845 | False | 1.050 |
| 4 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-02-17 | 0.963251 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.071852 | 5.04 | 3.0 | ... | 44 days | 0.014622 | 22.70 | -2.633147 | -2.563785 | 2.705450 | (0.95, 0.975] | 2.301503 | False | 0.975 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 3195881 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.044639 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.117063 | 1.52 | 0.0 | ... | 171 days | 0.014769 | 144.22 | -2.145043 | -2.132215 | 0.601630 | (1.025, 1.05] | 4.396845 | False | 1.050 |
| 3195882 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.052377 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.113900 | 1.52 | 0.0 | ... | 171 days | 0.014769 | 169.22 | -2.172434 | -2.165558 | 0.317525 | (1.05, 1.075] | 5.236635 | False | 1.075 |
| 3195883 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.060116 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.110925 | 1.52 | 20.0 | ... | 171 days | 0.014769 | 194.22 | -2.198901 | -2.199596 | -0.031616 | (1.05, 1.075] | 5.236635 | False | 1.075 |
| 3195884 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.067854 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.108540 | 1.52 | 0.0 | ... | 171 days | 0.014769 | 219.22 | -2.220637 | -2.234330 | -0.612848 | (1.05, 1.075] | 5.236635 | False | 1.075 |
| 3195885 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.075592 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.106814 | 1.52 | 0.0 | ... | 171 days | 0.014769 | 244.22 | -2.236666 | -2.269758 | -1.457925 | (1.075, 1.1] | 5.723928 | False | 1.100 |
2676696 rows × 26 columns
Construction of Monthly Leverage-Adjusted Portfolio Returns in CJS#
Process#
The construction of the 27 call and 27 put portfolios in CJS is a multi-step process, with the objective of developing portfolio returns series that are stationary and only moderately skewed. Note that the discrete bucketing of moneyness and days to maturity lead to multiple candidate options for each portfolio on each trading day. These options are given weights according to a bivariate Gaussian weighting kernel in moneyness and maturity (bandwidths: 0.0125 in moneyness and 10 days to maturity).
Each portfolio’s daily returns are initially calculated as simple arithmetic return, assuming the option is bought and sold at its bid-ask midpoint at each rebalancing. The one-day arithmetic return is then converted to a leverage-adjusted return. This procedure is achieved by calculating the one-day return of a hypothetical portfolio with \(\omega_{BSM}^{-1}\) dollars invested in the option, and \((1 - \omega^{-1})\) dollars invested in the risk-free rate, where \(\omega_{BSM}\) is the BSM elasticity based on the implied volatility of the option.
Each leverage-adjusted call portfolio comprises of a long position in a fraction of a call, and some investment in the risk-free rate.
Each leverage-adjusted put portfolio comprises of a short position in a fraction of a put, and >100% investment in the risk-free rate.
For clarity, we present below the mathematics behind CJS’ descriptions of the portfolio construction process. The following applies for a single trading day \(t\), for a set of candidate call or put options. Portfolios in CJS are identified by 3 characteristics: option type (call or put), moneyness (9 discrete targets), and time to maturity (3 discrete targets). On any given day, it is rare to find options that exactly match the moneyness and maturity targets. Instead, there may be multiple options that are “close to” the target moneyness / maturity (each a “candidate option”). Furthermore, each candidate option has its own price and price sensitivity to changes in the underlying SPX index level. In order to arrive at a “price” for an option portfolio, CJS applies a Gaussian weighting kernel in moneyness and maturity, as described below. This kernel-weighted price across the candidate options on a given day is used as the price of the option component of the portfolio (the other component being the risk-free rate). This portfolio is leverage-adjusted using the BSM elasticity, in order to standardize the sensitivity of OTM and ITM portfolios to changes in the underlying.
1. Gaussian Kernel Weighting#
Let:
\(m_{i}\) = moneyness of option \(i\)
\(\tau_{i}\) = days to maturity of option \(i\)
\(k_{s}\) = target moneyness
\(\tau\) = target maturity
\(h_{m}\), \(h_{\tau}\) = bandwidths for moneyness and maturity
\(d_{i}^2 = \left( \frac{m_{i} - k_{s}}{h_{m}} \right)^2 + \left( \frac{\tau_{i} - \tau}{h_{\tau}} \right)^2\)
Then the unnormalized Gaussian weight for option \(i\) is:
The normalized kernel weight:
2. Option Elasticity#
Let:
\(S_{t}\) = underlying index level at time \(t\)
\(P_{i}\) = price of option \(i\)
\(\Delta_{i}\) = option delta
Then:
3. Arithmetic Return of Option \(i\)#
Let:
\(P_{i,t-1}\) = price of option \(i\) at time \(t-1\)
\(P_{i,t}\) = price of option \(i\) at time \(t\)
Then:
4. Leverage-Adjusted Portfolio Construction#
Let:
\(r_{f}\) = risk-free rate on day \(t\)
The leverage-adjusted return of the call portfolio is:
The leverage-adjusted return of the put portfolio is:
Below we implement this process.
Implementation#
1. Build the FTSFA ID for each portfolio#
# identify the maturity ID based on the closest maturity to 30, 60, or 90 days
maturity_id = pd.concat(
(
abs(spx_filtered["days_to_maturity"].dt.days - 30),
abs(spx_filtered["days_to_maturity"].dt.days - 60),
abs(spx_filtered["days_to_maturity"].dt.days - 90),
),
axis=1,
)
maturity_id.columns = [30, 60, 90]
spx_filtered["maturity_id"] = maturity_id.idxmin(axis=1)
spx_filtered["ftfsa_id"] = (
spx_filtered["cp_flag"]
+ "_"
+ (spx_filtered["moneyness_id"] * 1000).apply(
lambda x: str(int(x)) if pd.notnull(x) and x == int(x) else str(x)
)
+ "_"
+ spx_filtered["maturity_id"].astype(str)
)
# set index to ftfsa_id and date
spx_filtered.set_index(["ftfsa_id", "date"], inplace=True)
spx_filtered
| exdate | moneyness | secid | open | close | cp_flag | IV | tb_m3 | volume | open_interest | ... | pc_parity_int_rate | intrinsic | log_iv | fitted_iv | rel_distance_iv | moneyness_bin | stdev_iv_moneyness_bin | is_outlier_iv | moneyness_id | maturity_id | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ftfsa_id | date | |||||||||||||||||||||
| C_1000_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 0.987534 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.082711 | 5.04 | 444.0 | 5905.0 | ... | 0.015898 | 7.70 | -2.492403 | -2.377298 | 4.841838 | (0.975, 1.0] | 3.516840 | False | 1.000 | 30 |
| C_1025_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 1.019913 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.097356 | 5.04 | 4022.0 | 5969.0 | ... | 0.015898 | 0.00 | -2.329381 | -2.285771 | 1.907866 | (1.0, 1.025] | 5.219336 | False | 1.025 | 30 |
| C_1050_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 1.028007 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.101756 | 5.04 | 1627.0 | 6224.0 | ... | 0.015898 | 0.00 | -2.285177 | -2.264082 | 0.931727 | (1.025, 1.05] | 4.396845 | False | 1.050 | 30 |
| 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 1.036102 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.100588 | 5.04 | 0.0 | 6593.0 | ... | 0.015898 | 0.00 | -2.296722 | -2.242870 | 2.401027 | (1.025, 1.05] | 4.396845 | False | 1.050 | 30 | |
| C_975_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-02-17 | 0.963251 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.071852 | 5.04 | 3.0 | 34.0 | ... | 0.014622 | 22.70 | -2.633147 | -2.563785 | 2.705450 | (0.95, 0.975] | 2.301503 | False | 0.975 | 30 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| P_1050_90 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.044639 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.117063 | 1.52 | 0.0 | 395.0 | ... | 0.014769 | 144.22 | -2.145043 | -2.132215 | 0.601630 | (1.025, 1.05] | 4.396845 | False | 1.050 | 90 |
| P_1075_90 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.052377 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.113900 | 1.52 | 0.0 | 163.0 | ... | 0.014769 | 169.22 | -2.172434 | -2.165558 | 0.317525 | (1.05, 1.075] | 5.236635 | False | 1.075 | 90 |
| 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.060116 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.110925 | 1.52 | 20.0 | 310.0 | ... | 0.014769 | 194.22 | -2.198901 | -2.199596 | -0.031616 | (1.05, 1.075] | 5.236635 | False | 1.075 | 90 | |
| 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.067854 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.108540 | 1.52 | 0.0 | 12.0 | ... | 0.014769 | 219.22 | -2.220637 | -2.234330 | -0.612848 | (1.05, 1.075] | 5.236635 | False | 1.075 | 90 | |
| P_1100_90 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.075592 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.106814 | 1.52 | 0.0 | 0.0 | ... | 0.014769 | 244.22 | -2.236666 | -2.269758 | -1.457925 | (1.075, 1.1] | 5.723928 | False | 1.100 | 90 |
2676696 rows × 26 columns
portfolio_ids = spx_filtered.index.get_level_values("ftfsa_id").unique()
portfolio_ids
Index(['C_1000_30', 'C_1025_30', 'C_1050_30', 'C_975_30', 'C_1075_30',
'C_950_60', 'C_975_60', 'C_1000_60', 'C_1025_60', 'C_1050_60',
'C_1075_60', 'C_1100_30', 'C_900_60', 'C_925_60', 'C_950_30',
'C_1100_60', 'C_925_30', 'C_900_30', 'C_900_90', 'C_925_90', 'C_950_90',
'C_975_90', 'C_1050_90', 'C_1000_90', 'C_1025_90', 'C_1075_90',
'C_1100_90', 'P_1000_30', 'P_1025_30', 'P_1050_30', 'P_975_30',
'P_1075_30', 'P_950_60', 'P_975_60', 'P_1000_60', 'P_1025_60',
'P_1050_60', 'P_1075_60', 'P_1100_30', 'P_900_60', 'P_925_60',
'P_950_30', 'P_1100_60', 'P_925_30', 'P_900_30', 'P_900_90', 'P_925_90',
'P_950_90', 'P_975_90', 'P_1050_90', 'P_1000_90', 'P_1025_90',
'P_1075_90', 'P_1100_90'],
dtype='object', name='ftfsa_id')
spx_filtered["days_to_maturity"].describe()
count 2676696
mean 56 days 07:55:28.214186444
std 36 days 18:30:26.100585916
min 7 days 00:00:00
25% 29 days 00:00:00
50% 49 days 00:00:00
75% 74 days 00:00:00
max 180 days 00:00:00
Name: days_to_maturity, dtype: object
2. Calculate option elasticity and daily kernel weighting for candidate options for each portfolio.#
spx_mod = spx_filtered.copy()
# calculate option delta and elasticity
spx_mod = calc_option_delta_elasticity(spx_mod)
# calculate daily kernel weights for candidate options
spx_mod = calc_kernel_weights(spx_mod)
spx_mod
| ftfsa_id | date | exdate | moneyness | secid | open | close | cp_flag | IV | tb_m3 | ... | rel_distance_iv | moneyness_bin | stdev_iv_moneyness_bin | is_outlier_iv | moneyness_id | maturity_id | option_delta | option_elasticity | days_to_maturity_int | kernel_weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | C_1000_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 0.987534 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.082711 | 5.04 | ... | 4.841838 | (0.975, 1.0] | 3.516840 | False | 1.000 | 30 | 0.805272 | 48.826136 | 16 | 4.123556e-01 |
| 1 | C_1025_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 1.019913 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.097356 | 5.04 | ... | 1.907866 | (1.0, 1.025] | 5.219336 | False | 1.025 | 30 | 0.198018 | 95.465702 | 16 | 1.000000e+00 |
| 2 | C_1050_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 1.028007 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.101756 | 5.04 | ... | 0.931727 | (1.025, 1.05] | 4.396845 | False | 1.050 | 30 | 0.118568 | 106.529727 | 16 | 2.829909e-01 |
| 3 | C_1050_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 1.036102 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.100588 | 5.04 | ... | 2.401027 | (1.025, 1.05] | 4.396845 | False | 1.050 | 30 | 0.058374 | 128.204965 | 16 | 7.170091e-01 |
| 4 | C_975_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-02-17 | 0.963251 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.071852 | 5.04 | ... | 2.705450 | (0.95, 0.975] | 2.301503 | False | 0.975 | 30 | 0.960529 | 23.041498 | 44 | 4.015525e-01 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2676691 | P_1050_90 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.044639 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.117063 | 1.52 | ... | 0.601630 | (1.025, 1.05] | 4.396845 | False | 1.050 | 90 | -0.661333 | -11.093570 | 171 | 5.365533e-16 |
| 2676692 | P_1075_90 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.052377 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.113900 | 1.52 | ... | 0.317525 | (1.05, 1.075] | 5.236635 | False | 1.075 | 90 | -0.700041 | -10.839582 | 171 | 1.775800e-16 |
| 2676693 | P_1075_90 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.060116 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.110925 | 1.52 | ... | -0.031616 | (1.05, 1.075] | 5.236635 | False | 1.075 | 90 | -0.737984 | -10.556841 | 171 | 4.495126e-16 |
| 2676694 | P_1075_90 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.067854 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.108540 | 1.52 | ... | -0.612848 | (1.05, 1.075] | 5.236635 | False | 1.075 | 90 | -0.773579 | -10.226122 | 171 | 7.756405e-16 |
| 2676695 | P_1100_90 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-06-19 | 1.075592 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.106814 | 1.52 | ... | -1.457925 | (1.075, 1.1] | 5.723928 | False | 1.100 | 90 | -0.805867 | -9.854573 | 171 | 3.015839e-16 |
2676696 rows × 32 columns
print("Kernel weight check: All portfolios should sum to 1.0.")
spx_mod.groupby(["date", "ftfsa_id"])["kernel_weight"].sum().round(15).value_counts()
Kernel weight check: All portfolios should sum to 1.0.
kernel_weight
1.0 156522
Name: count, dtype: int64
3. Remove options from the portfolio with weights lower than 1%#
spx_mod = spx_mod[spx_mod["kernel_weight"] >= 0.01].reset_index(drop=True)
spx_mod
| ftfsa_id | date | exdate | moneyness | secid | open | close | cp_flag | IV | tb_m3 | ... | rel_distance_iv | moneyness_bin | stdev_iv_moneyness_bin | is_outlier_iv | moneyness_id | maturity_id | option_delta | option_elasticity | days_to_maturity_int | kernel_weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | C_1000_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 0.987534 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.082711 | 5.04 | ... | 4.841838 | (0.975, 1.0] | 3.516840 | False | 1.000 | 30 | 0.805272 | 48.826136 | 16 | 0.412356 |
| 1 | C_1025_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 1.019913 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.097356 | 5.04 | ... | 1.907866 | (1.0, 1.025] | 5.219336 | False | 1.025 | 30 | 0.198018 | 95.465702 | 16 | 1.000000 |
| 2 | C_1050_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 1.028007 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.101756 | 5.04 | ... | 0.931727 | (1.025, 1.05] | 4.396845 | False | 1.050 | 30 | 0.118568 | 106.529727 | 16 | 0.282991 |
| 3 | C_1050_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-01-20 | 1.036102 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.100588 | 5.04 | ... | 2.401027 | (1.025, 1.05] | 4.396845 | False | 1.050 | 30 | 0.058374 | 128.204965 | 16 | 0.717009 |
| 4 | C_975_30 | 1996-01-04 | 1996-02-17 | 0.963251 | 108105.0 | 621.32 | 617.70 | C | 0.071852 | 5.04 | ... | 2.705450 | (0.95, 0.975] | 2.301503 | False | 0.975 | 30 | 0.960529 | 23.041498 | 44 | 0.401552 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 1926209 | P_1100_90 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-03-31 | 1.077139 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.102622 | 1.52 | ... | -2.816445 | (1.075, 1.1] | 5.723928 | False | 1.100 | 90 | -0.911590 | -11.547335 | 91 | 0.066978 |
| 1926210 | P_1100_90 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-03-31 | 1.080234 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.099399 | 1.52 | ... | -2.052300 | (1.075, 1.1] | 5.723928 | False | 1.100 | 90 | -0.927007 | -11.357435 | 91 | 0.102163 |
| 1926211 | P_1100_90 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-03-31 | 1.083330 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.102206 | 1.52 | ... | -3.820268 | (1.075, 1.1] | 5.723928 | False | 1.100 | 90 | -0.929031 | -10.968371 | 91 | 0.146563 |
| 1926212 | P_1100_90 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-03-31 | 1.091068 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.103736 | 1.52 | ... | -5.884824 | (1.075, 1.1] | 5.723928 | False | 1.100 | 90 | -0.943358 | -10.241205 | 91 | 0.276281 |
| 1926213 | P_1100_90 | 2019-12-31 | 2020-03-31 | 1.098806 | 108105.0 | 3215.18 | 3230.78 | P | 0.105558 | 1.52 | ... | -8.008885 | (1.075, 1.1] | 5.723928 | False | 1.100 | 90 | -0.954434 | -9.582242 | 91 | 0.355017 |
1926214 rows × 32 columns
# check elasticity > 1 for call options and < -1 for put options
print("Elasticity > 1 for call options?")
spx_mod[spx_mod["cp_flag"] == "C"]["option_elasticity"].describe()["min"] > 1.0
Elasticity > 1 for call options?
np.True_
print("Elasticity < -1 for put options?")
spx_mod[spx_mod["cp_flag"] == "P"]["option_elasticity"].describe()["max"] < -1.0
Elasticity < -1 for put options?
np.True_
4. Calculate the daily arithmetic return and the leverage-adjusted return of each portfolio.#
On each trading day, the return of a portfolio is calculated as the weighted average return of the set of candidate options that comprise a single day’s option portfolio. The weighting used is the Gaussian kernel weight calculated earlier. Thus the daily return from period \(t\) to \(t+1\) represents the return from holding a set of candidate options, weighted using the kernel weights as of \(t\), from period \(t\) to \(t+1\).
portfolio_returns = compute_cjs_return_leverage_investment(spx_mod)
# Preview result
portfolio_returns.set_index(["date", "ftfsa_id"], inplace=True)
portfolio_returns = portfolio_returns.pivot_table(
index="date", columns="ftfsa_id", values="portfolio_return"
)
# daily_returns = pd.DataFrame(np.where(portfolio_returns > 1.0, np.nan, portfolio_returns), index=portfolio_returns.index, columns=portfolio_returns.columns)
daily_returns = portfolio_returns.copy()
daily_returns
| ftfsa_id | C_1000_30 | C_1000_60 | C_1000_90 | C_1025_30 | C_1025_60 | C_1025_90 | C_1050_30 | C_1050_60 | C_1050_90 | C_1075_30 | ... | P_900_90 | P_925_30 | P_925_60 | P_925_90 | P_950_30 | P_950_60 | P_950_90 | P_975_30 | P_975_60 | P_975_90 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| date | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1996-01-04 | 0.002171 | NaN | NaN | 0.000198 | NaN | NaN | -0.003106 | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | 0.003393 | NaN | NaN |
| 1996-01-05 | NaN | NaN | NaN | -0.002985 | NaN | NaN | 0.004674 | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 1996-01-09 | -0.004362 | -0.005736 | NaN | 0.011077 | 0.000193 | NaN | 0.039018 | 0.000195 | NaN | 0.008154 | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | 0.000191 | NaN | 0.011241 | 0.007766 | NaN |
| 1996-01-10 | -0.001291 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | -0.003064 | NaN | NaN | -0.005087 | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 1996-01-22 | -0.002792 | NaN | NaN | -0.004186 | NaN | NaN | 0.004054 | NaN | NaN | 0.016734 | ... | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2019-12-24 | NaN | NaN | NaN | -0.001959 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | 0.000877 | NaN | 0.000702 | -0.003096 | NaN | NaN | 0.007690 | -0.007144 | NaN | NaN |
| 2019-12-26 | 0.000177 | -0.000588 | -0.001565 | 0.049612 | 0.000451 | -0.001096 | 0.001201 | 0.000729 | NaN | 0.001499 | ... | 0.000925 | 0.000619 | 0.000816 | 0.001072 | 0.000456 | 0.000826 | 0.000696 | 0.002388 | 0.000837 | 0.000776 |
| 2019-12-27 | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | NaN | ... | 0.001085 | NaN | 0.000463 | 0.002847 | NaN | NaN | 0.002921 | NaN | NaN | NaN |
| 2019-12-30 | 0.000195 | -0.000363 | -0.000944 | 0.000539 | 0.000115 | -0.001000 | 0.001502 | -0.000179 | -0.001638 | 0.000554 | ... | 0.001061 | 0.000485 | 0.000862 | 0.000741 | 0.000373 | 0.000779 | 0.000816 | 0.000222 | 0.000845 | 0.001032 |
| 2019-12-31 | 0.000164 | -0.000746 | -0.001073 | 0.000216 | -0.000542 | -0.001064 | 0.000767 | -0.000273 | -0.000936 | 0.000142 | ... | 0.000913 | 0.000537 | 0.000821 | 0.000914 | 0.000592 | 0.000825 | 0.000898 | 0.000382 | 0.000766 | 0.000936 |
3740 rows × 54 columns
5. (to be implemented) Filling NaNs#
CJS implement an multi-step process to deal with options with missing prices (detailed in section 1.3 Portfolio Formation of the paper). We reserve the implementation this NaN-filling process for a future version of this dataset. For the current version, we compound the daily portfolio returns into monthly returns, which is the final form of the data utilized in the paper.
6. Compound Daily Portfolio Returns to Monthly (final 54 portfolios in CJS)#
cjs_returns = daily_returns.resample("M").apply(lambda x: (1 + x).prod() - 1)
cjs_returns = cjs_returns.reset_index().melt(
id_vars="date", var_name="ftfsa_id", value_name="return"
)
cjs_returns["ftfsa_id"] = "cjs_" + cjs_returns["ftfsa_id"]
cjs_returns = cjs_returns[["ftfsa_id", "date", "return"]].set_index(
["ftfsa_id", "date"]
)
# save to data directory
cjs_returns.to_parquet(
DATA_DIR / "options" / f"cjs_portfolio_returns_{DATE_RANGE}.parquet", index=True
)
cjs_returns
| return | ||
|---|---|---|
| ftfsa_id | date | |
| cjs_C_1000_30 | 1996-01-31 | -0.006272 |
| 1996-02-29 | 0.002888 | |
| 1996-03-31 | -0.002462 | |
| 1996-04-30 | 0.036055 | |
| 1996-05-31 | 0.003906 | |
| ... | ... | ... |
| cjs_P_975_90 | 2019-08-31 | 0.007421 |
| 2019-09-30 | 0.000517 | |
| 2019-10-31 | 0.138853 | |
| 2019-11-30 | 0.009941 | |
| 2019-12-31 | 0.007702 |
15552 rows × 1 columns
Construction of 18 Portfolio Return Series in He, Kelly, Manela (HKM 2017)#
HKM 2017 reduces the 54 portfolio return series constructed in CJS to 18 by taking an equal-weight average across the 3 maturities for the CJS portfolios with the same moneyness. Below we implement that procedure to obtain the final return series for the FTSFA.
hkm_returns = cjs_returns.copy().reset_index()
hkm_returns = hkm_returns.assign(
type=hkm_returns["ftfsa_id"].apply(lambda x: x.split("_")[1]),
moneyness_id=hkm_returns["ftfsa_id"].apply(lambda x: x.split("_")[2]),
maturity_id=hkm_returns["ftfsa_id"].apply(lambda x: x.split("_")[3]),
)
hkm_returns.drop(columns=["ftfsa_id"], inplace=True)
hkm_returns.set_index(["date", "type", "moneyness_id", "maturity_id"], inplace=True)
hkm_returns = hkm_returns.groupby(["date", "type", "moneyness_id"]).mean()
hkm_returns["ftfsa_id"] = (
"hkm_"
+ hkm_returns.index.get_level_values("type")
+ "_"
+ hkm_returns.index.get_level_values("moneyness_id")
)
hkm_returns = (
hkm_returns.reset_index()
.drop(columns=["type", "moneyness_id"])
.set_index(["ftfsa_id", "date"])
.sort_index()
)
# save to data directory
hkm_returns.to_parquet(
DATA_DIR / "options" / f"hkm_portfolio_returns_{DATE_RANGE}.parquet", index=True
)
hkm_returns
| return | ||
|---|---|---|
| ftfsa_id | date | |
| hkm_C_1000 | 1996-01-31 | -0.004002 |
| 1996-02-29 | -0.000919 | |
| 1996-03-31 | -0.000821 | |
| 1996-04-30 | 0.012018 | |
| 1996-05-31 | 0.000912 | |
| ... | ... | ... |
| hkm_P_975 | 2019-08-31 | 0.013859 |
| 2019-09-30 | 0.006864 | |
| 2019-10-31 | 0.050960 | |
| 2019-11-30 | 0.010639 | |
| 2019-12-31 | 0.000444 |
5184 rows × 1 columns
Portfolio Returns Analysis#
The objective of the data filtration process was to create portfolios whose returns were close to normal and only moderately skewed. Based on the process we implemented, we observed the following in the 54 CJS portfolios and 18 HKM portfolios.
Normality:
CJS: virtually all portfolios reject normality.
HKM: a few portfolios might plausibly be normal (higher Jarque-Bera and Normaltest p-values).
Skewness: Both CJS and HKM have generally positive skew, with HKM portfolios showing a wider dispersion, with some portfolios extremely right-skewed.
Kurtosis:
CJS: heavier tails on average (median 4.6).
HKM: median closer to normal (3.1), but with some extreme outliers (kurtosis > 100).
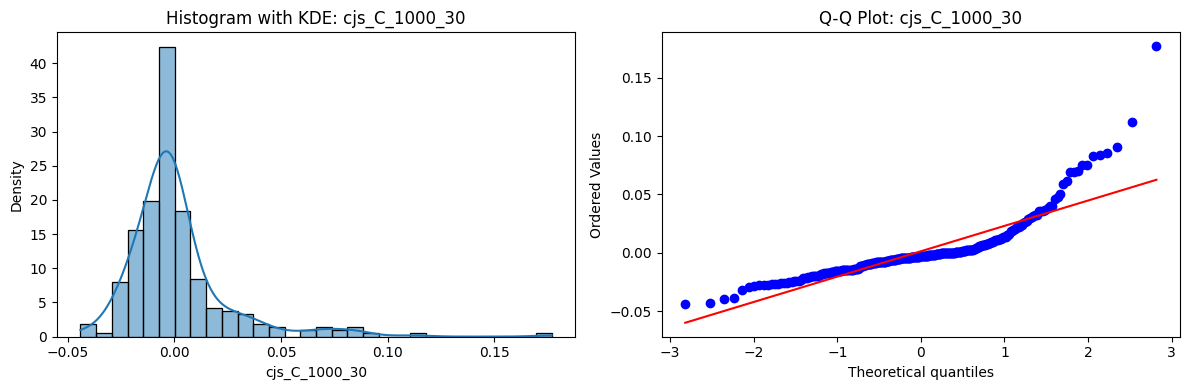
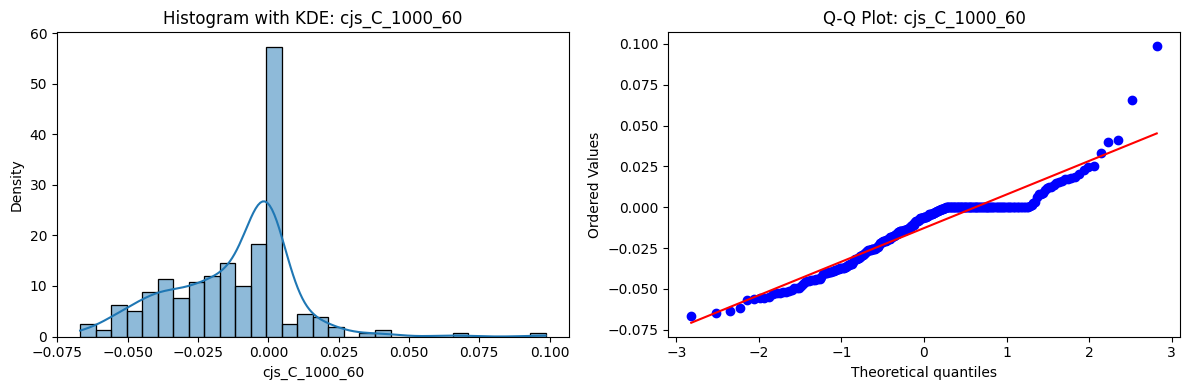
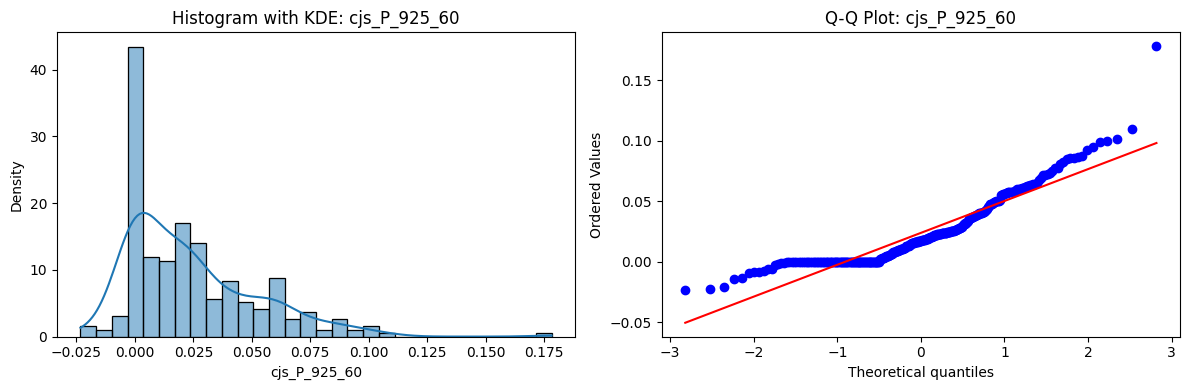
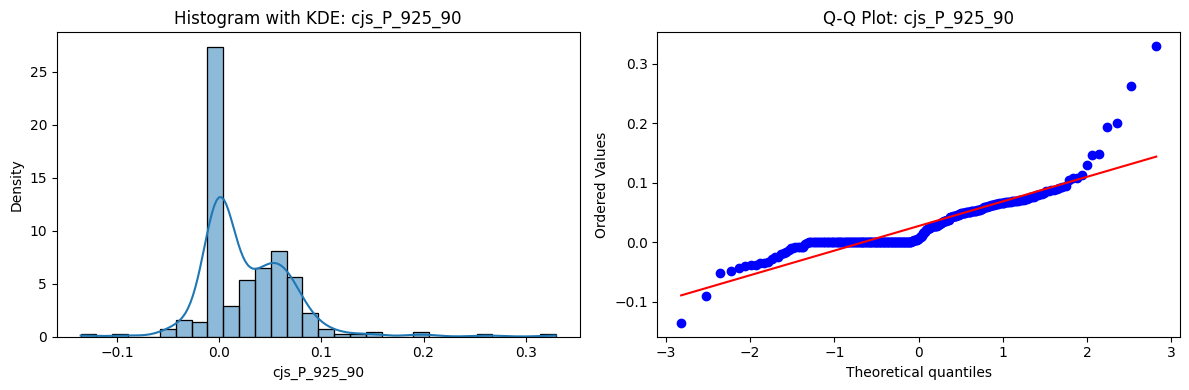
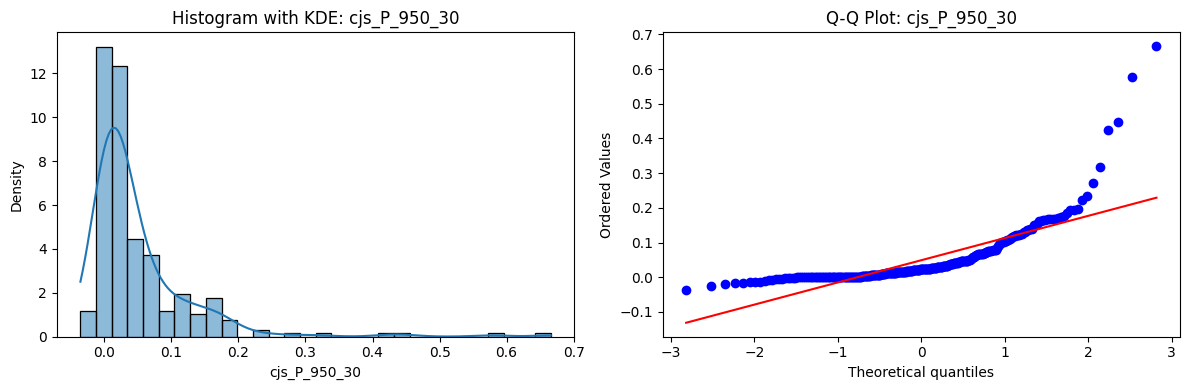
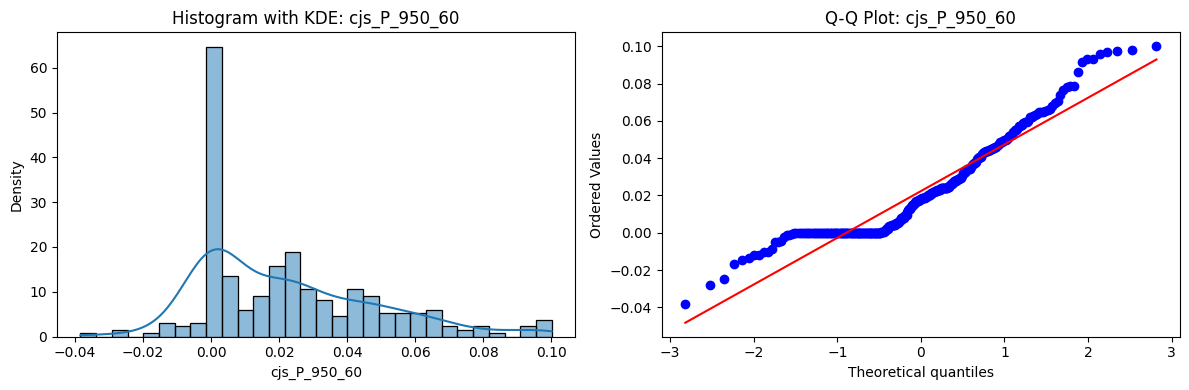
Tests for Normality of Returns in the 54 CJS Portfolios#
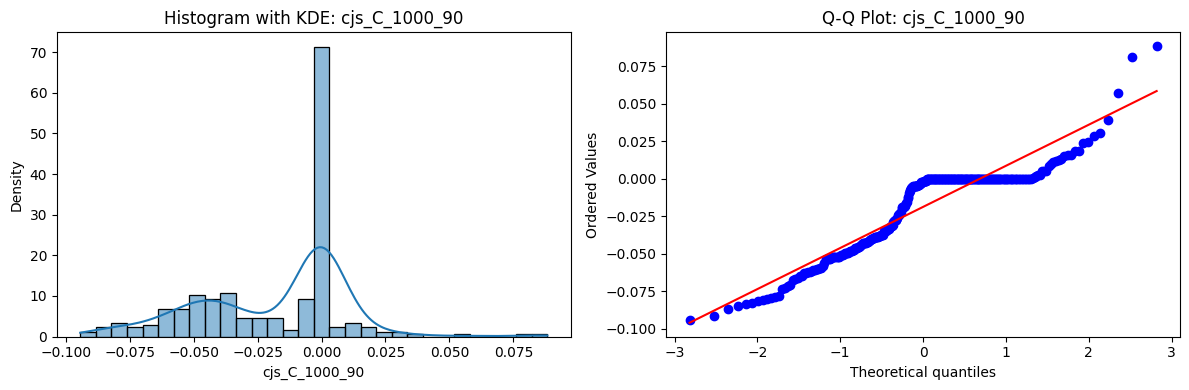
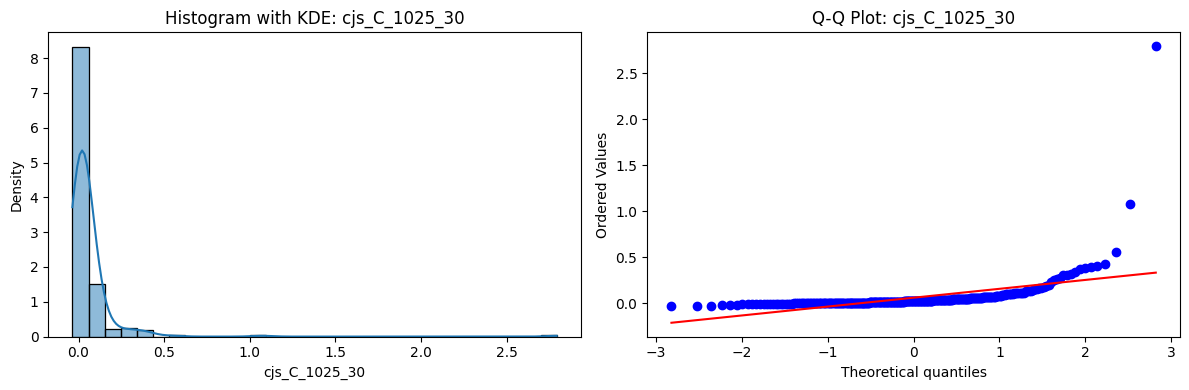
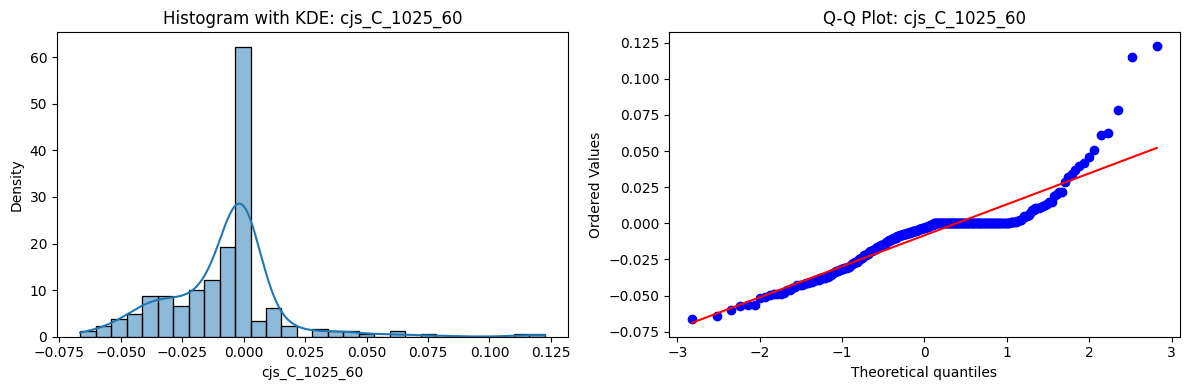
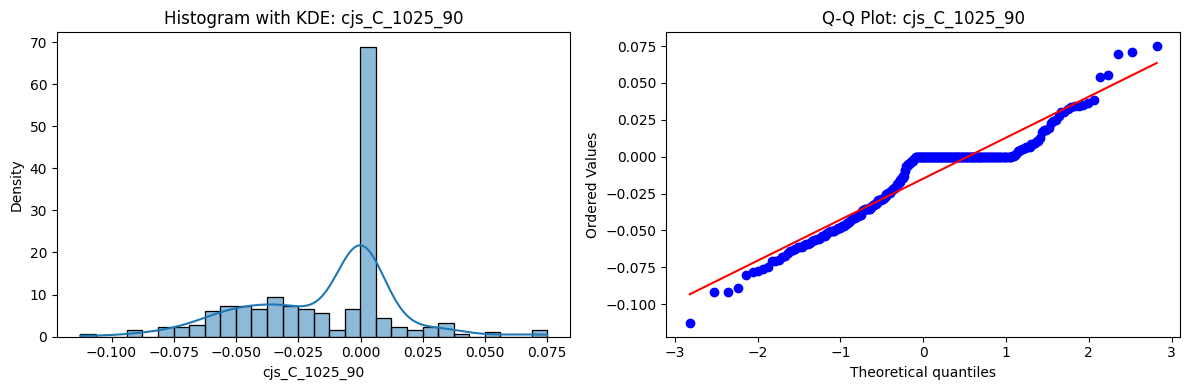
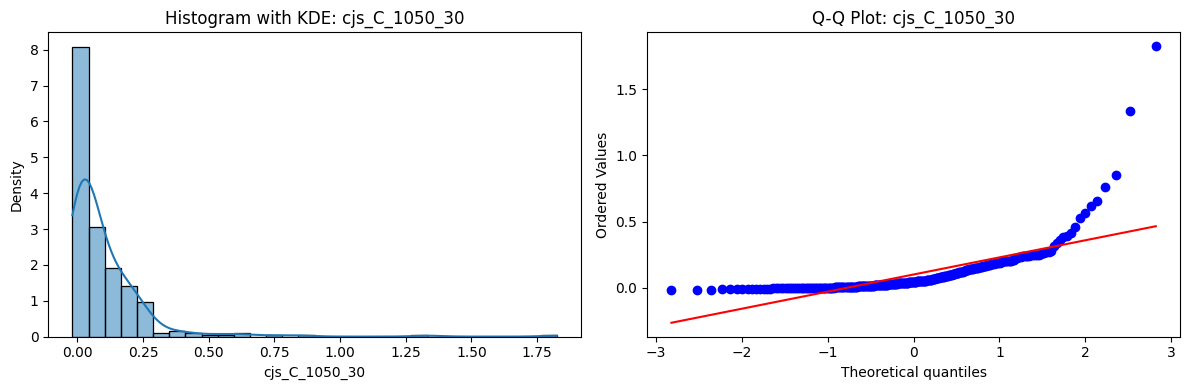
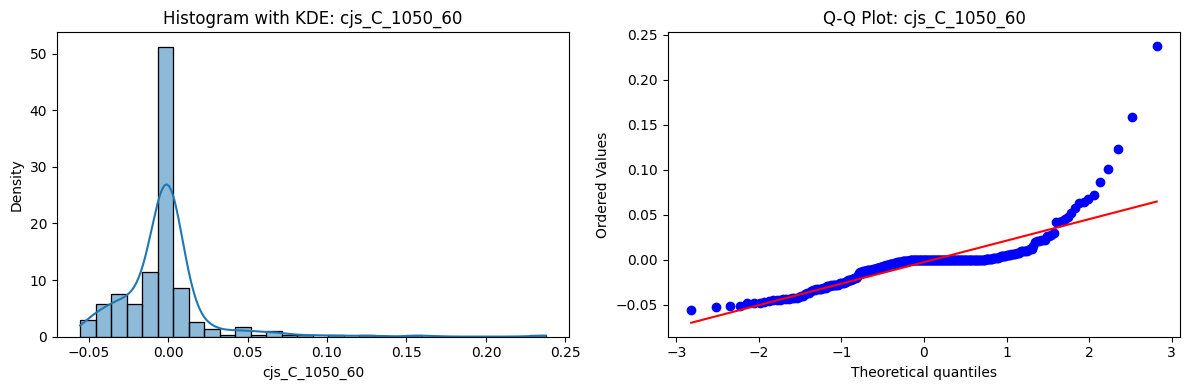
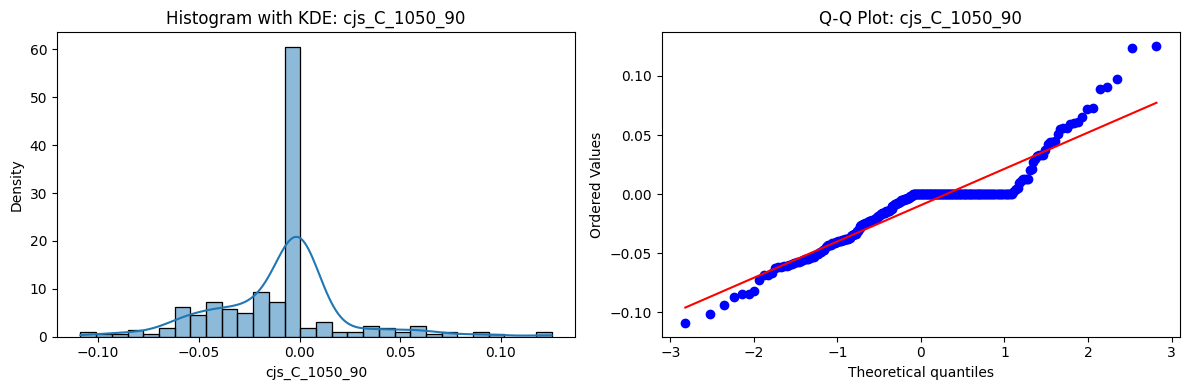
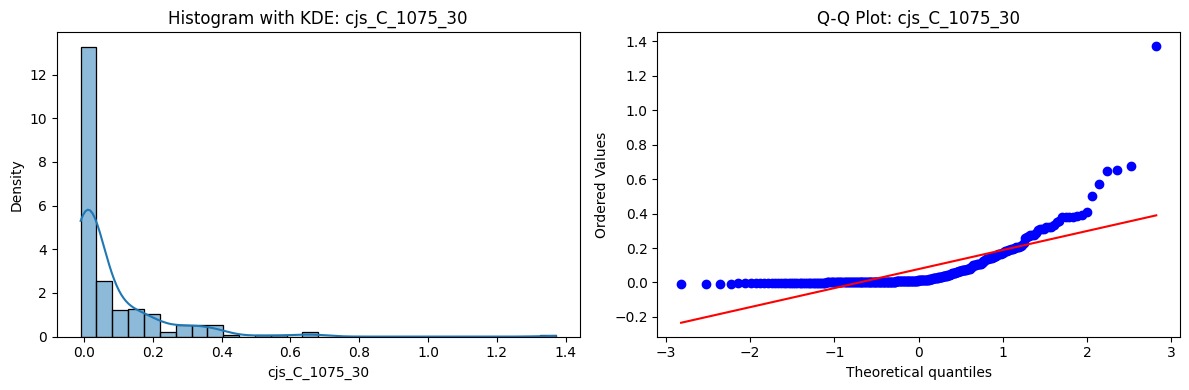
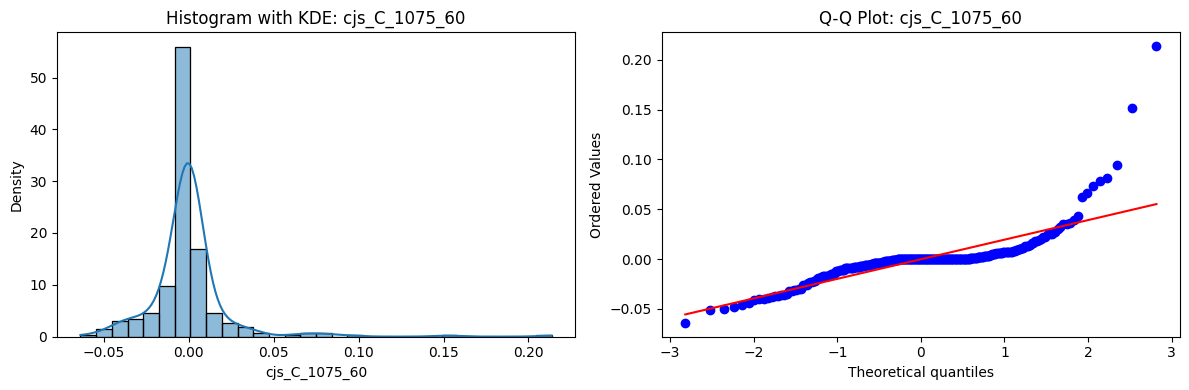
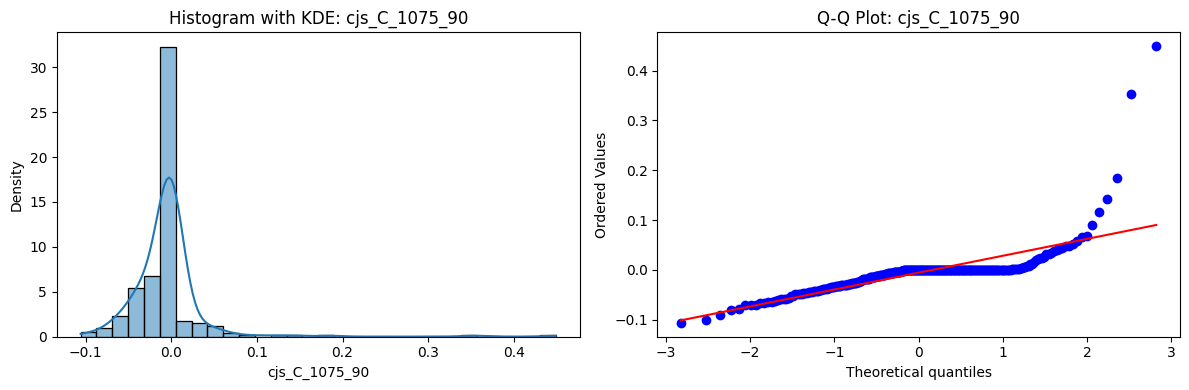
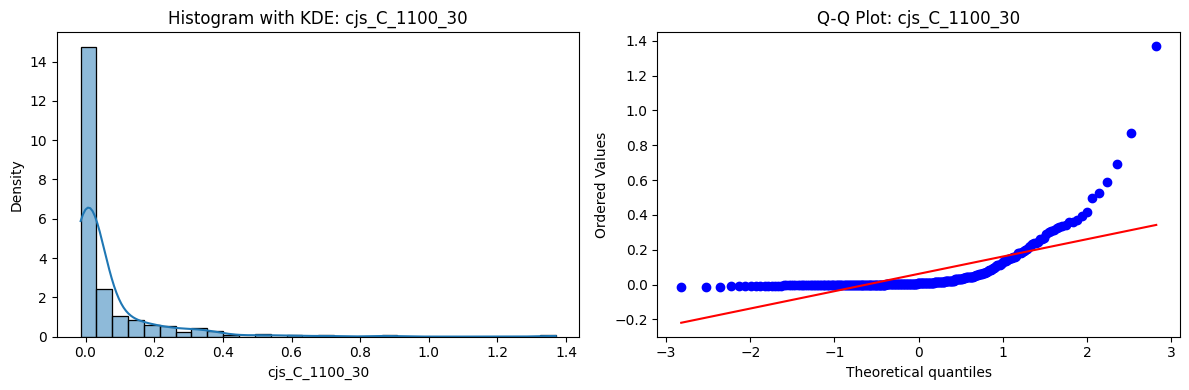
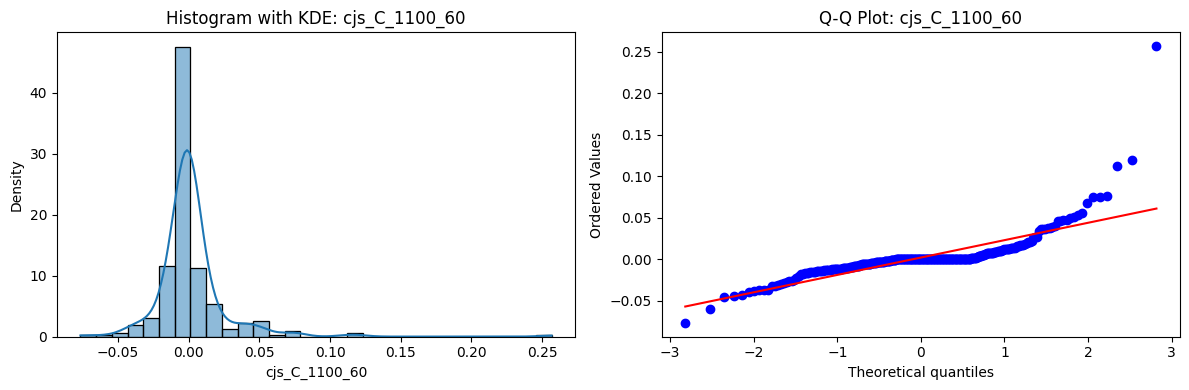
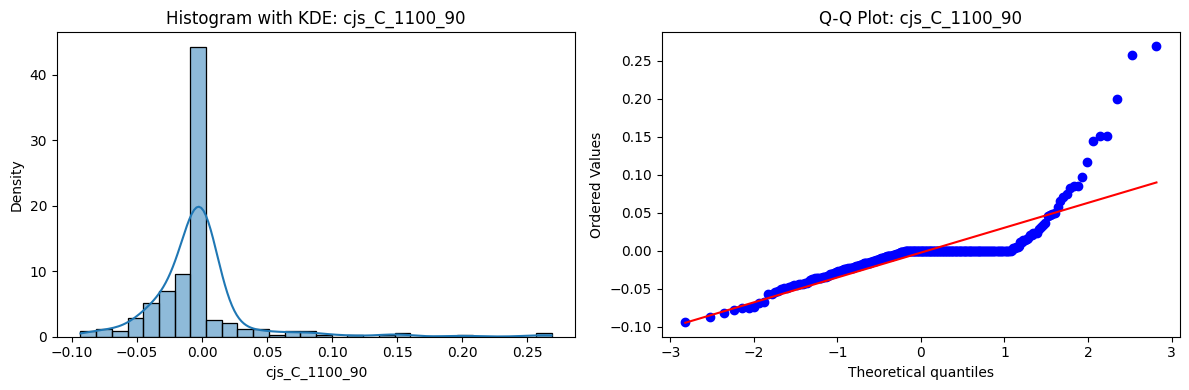
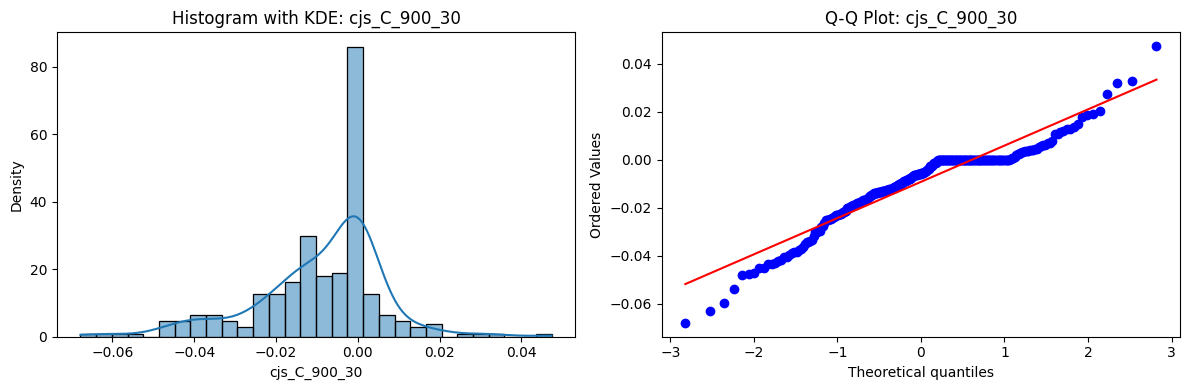
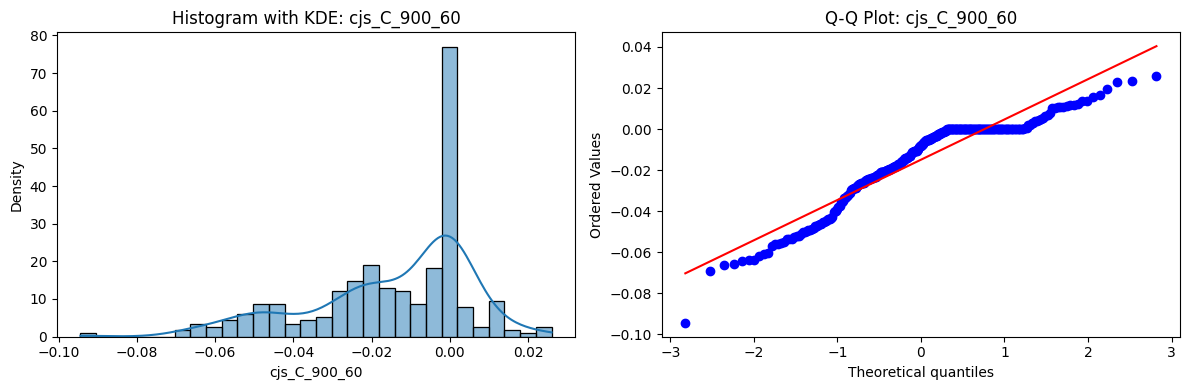
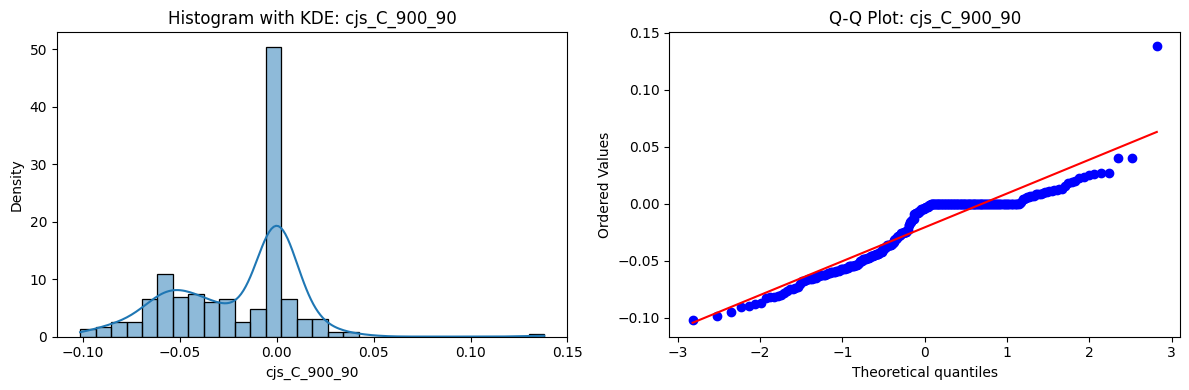
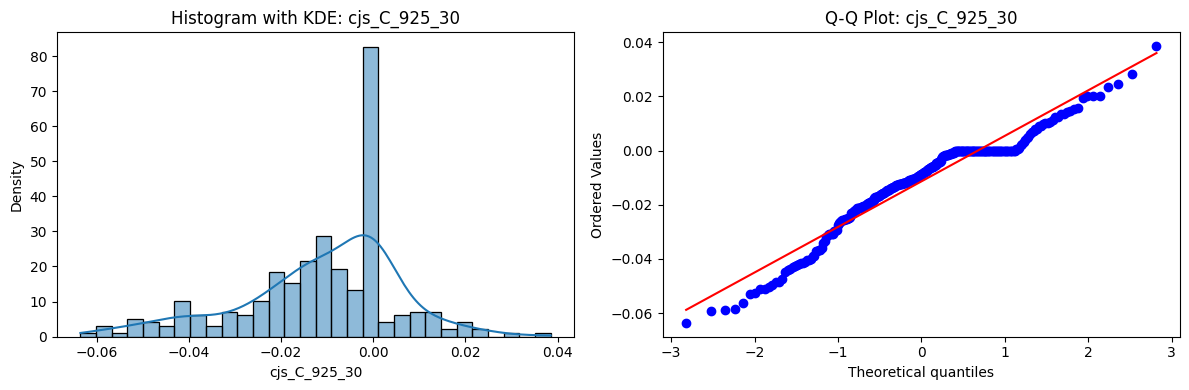
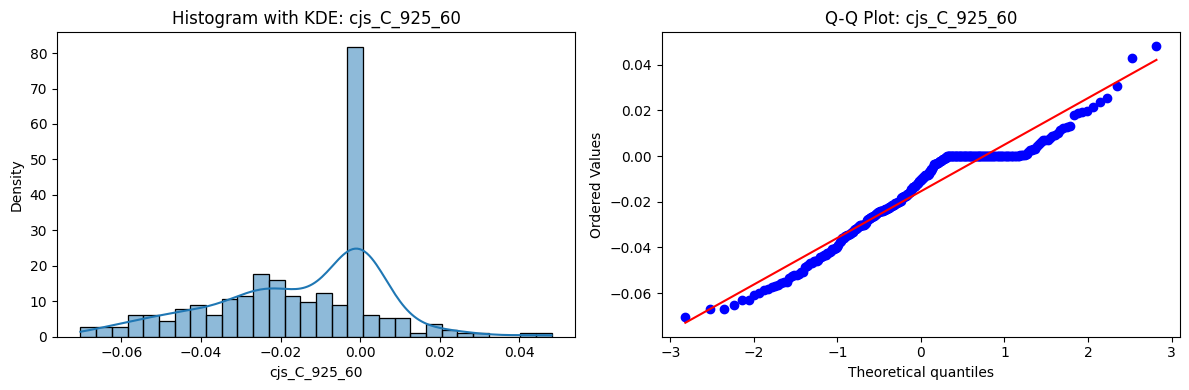
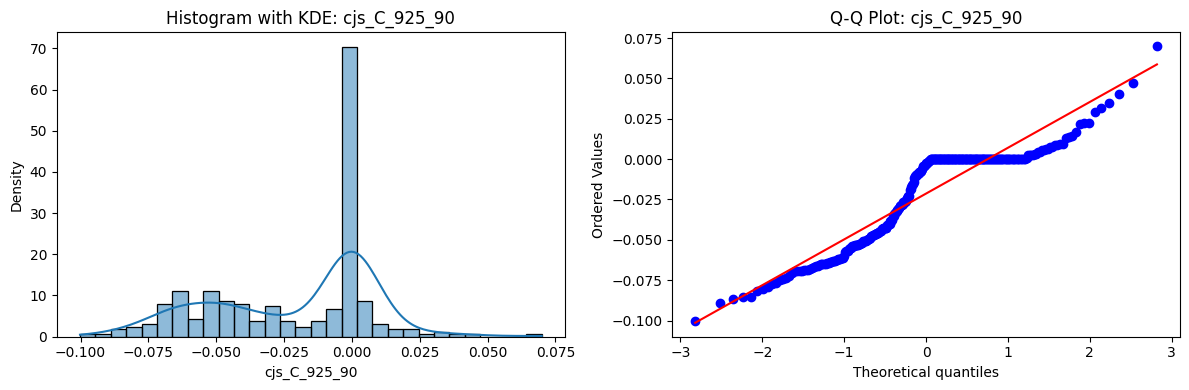
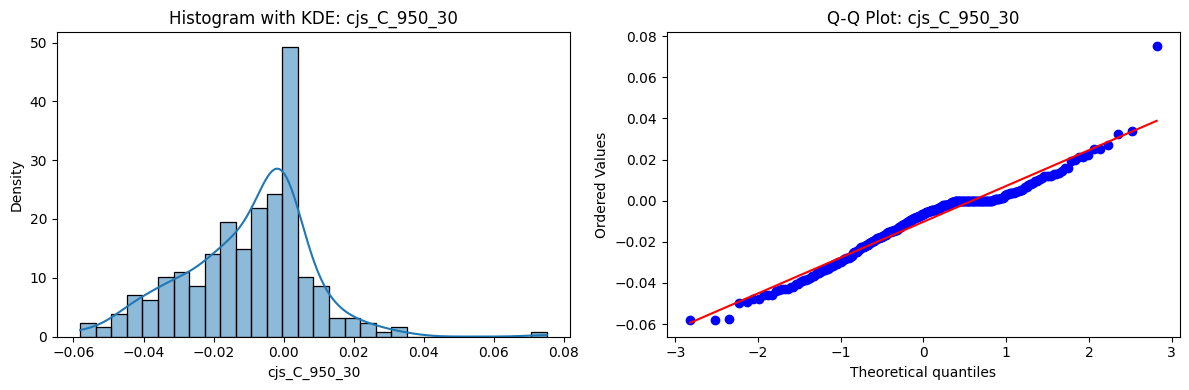
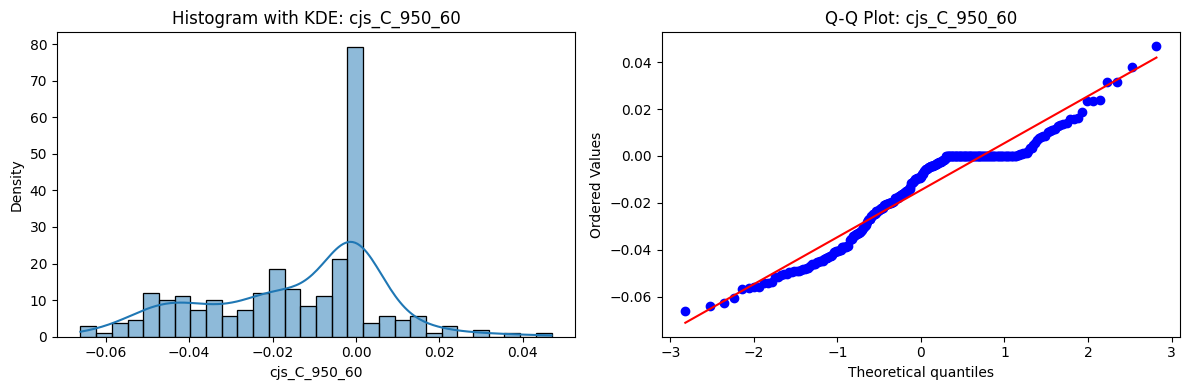
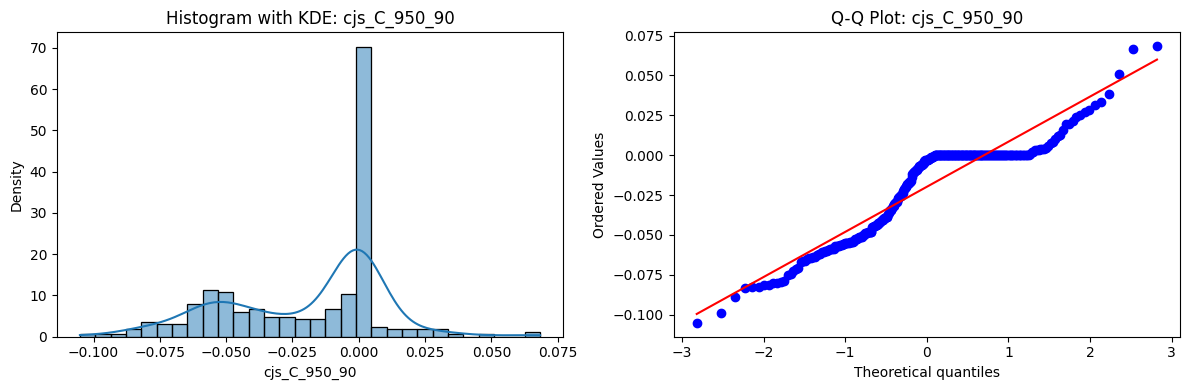
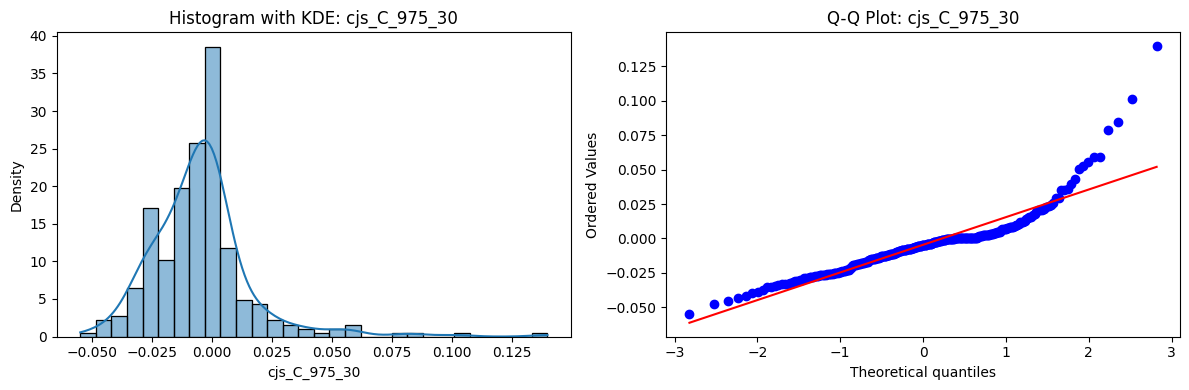
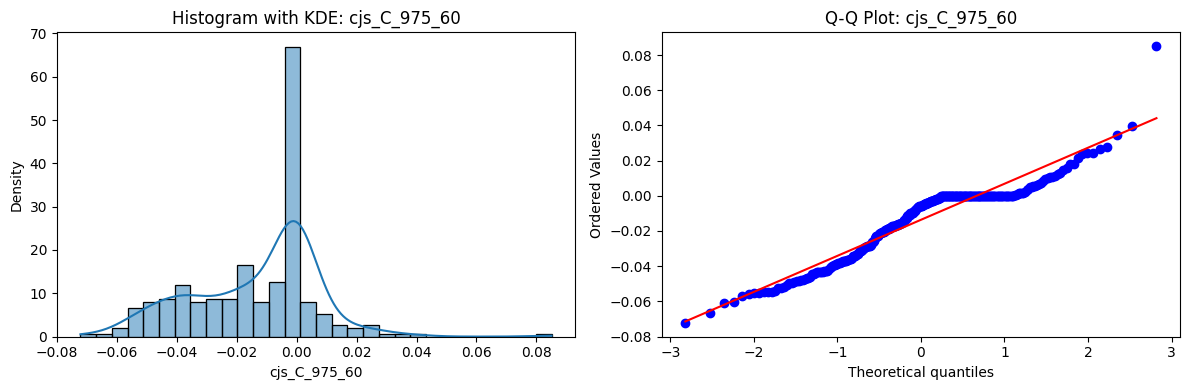
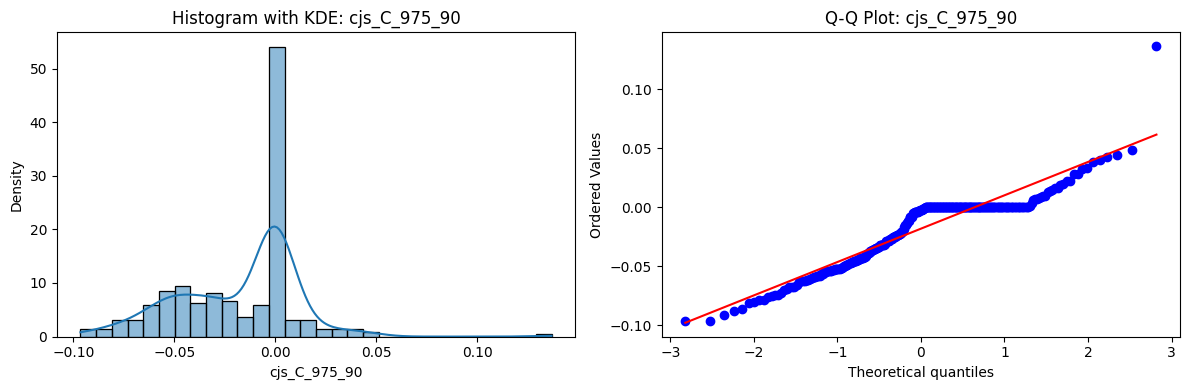
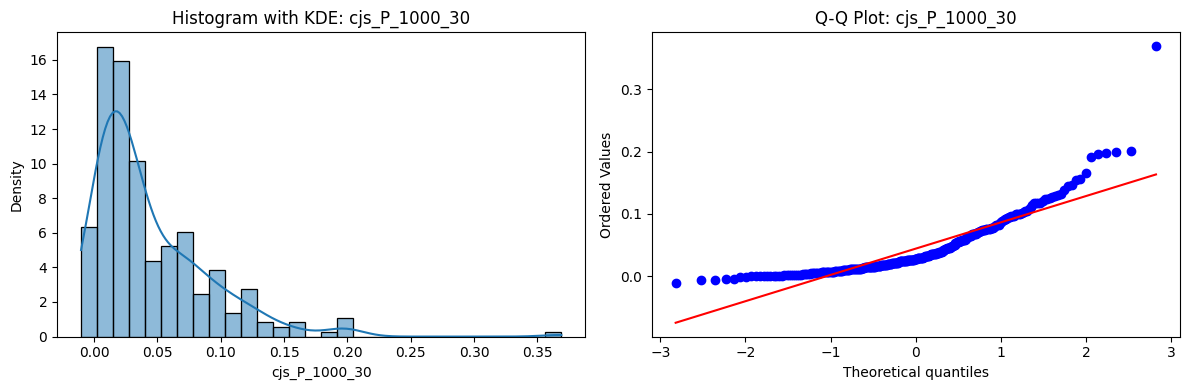
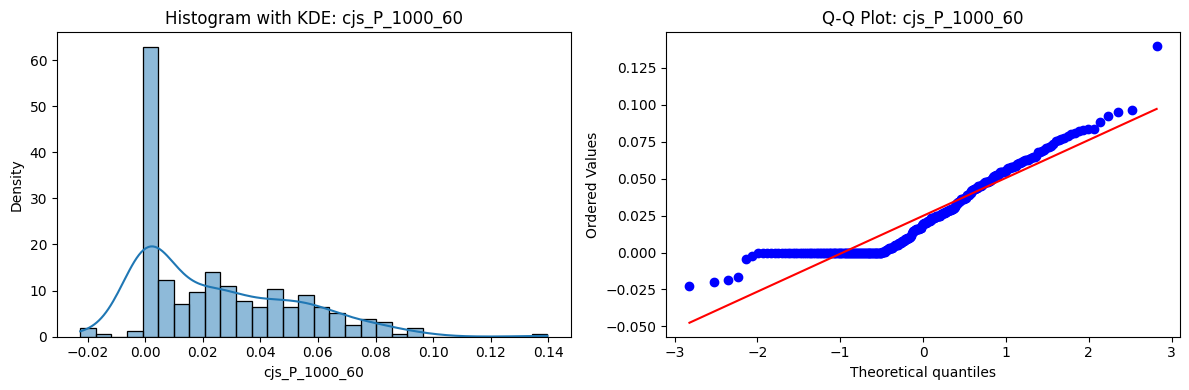
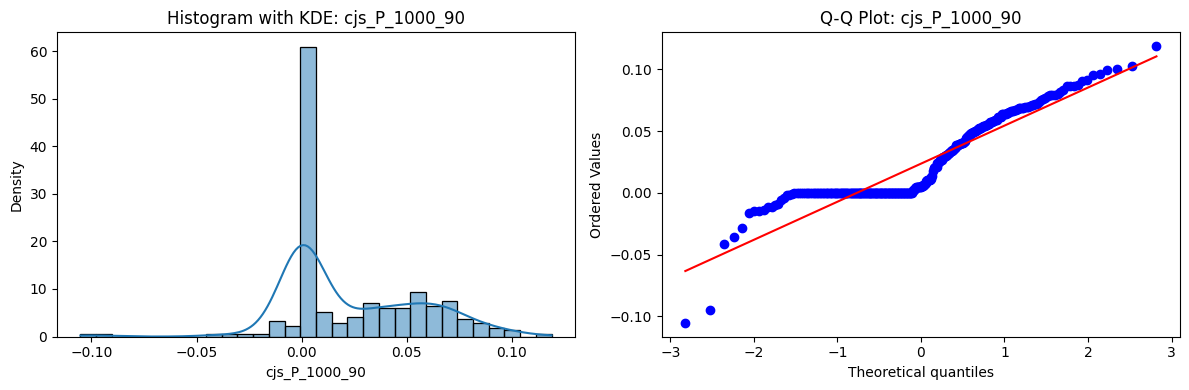
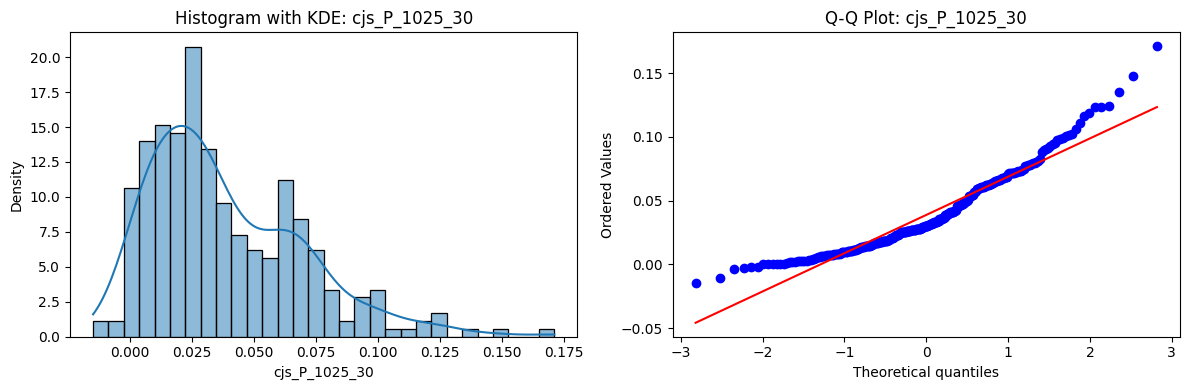
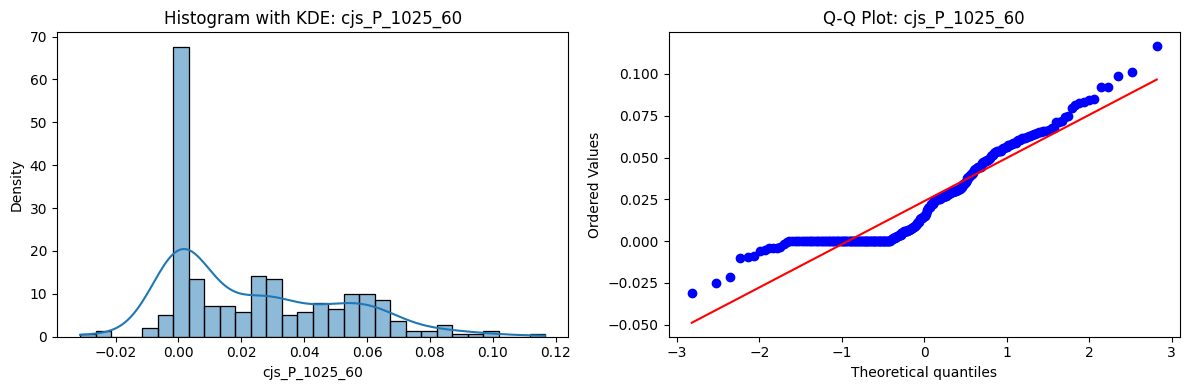
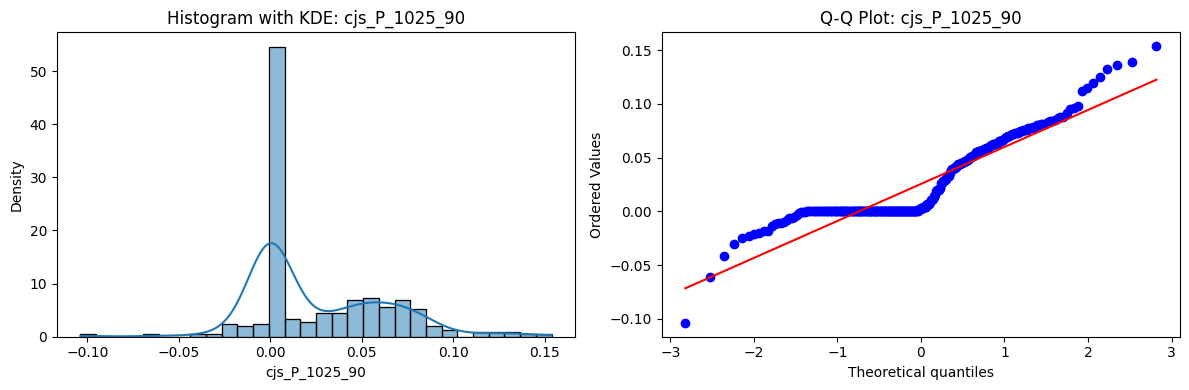
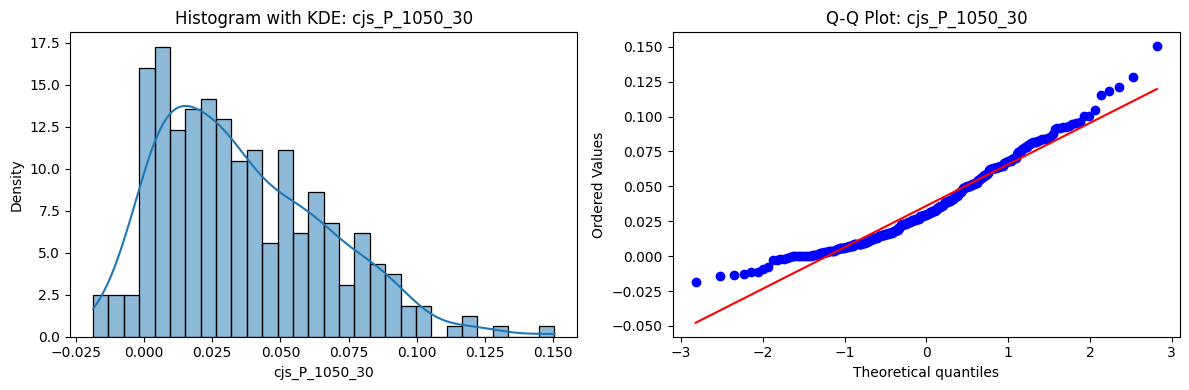
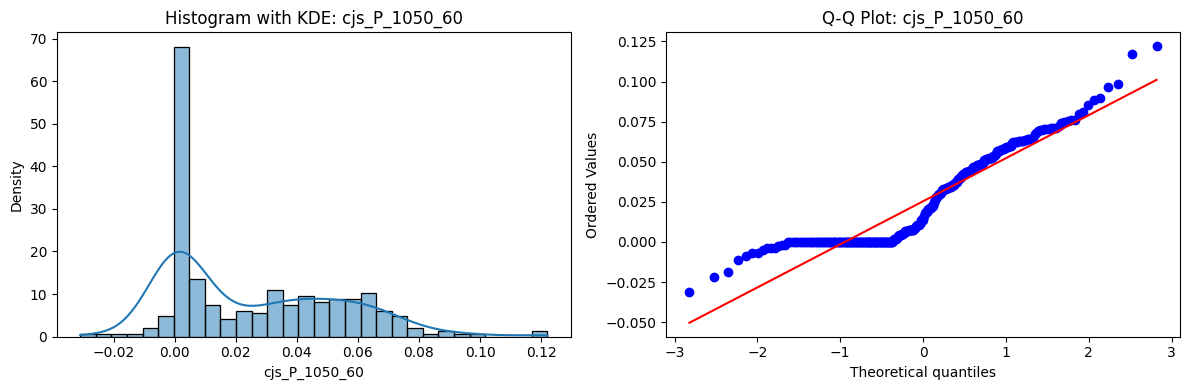
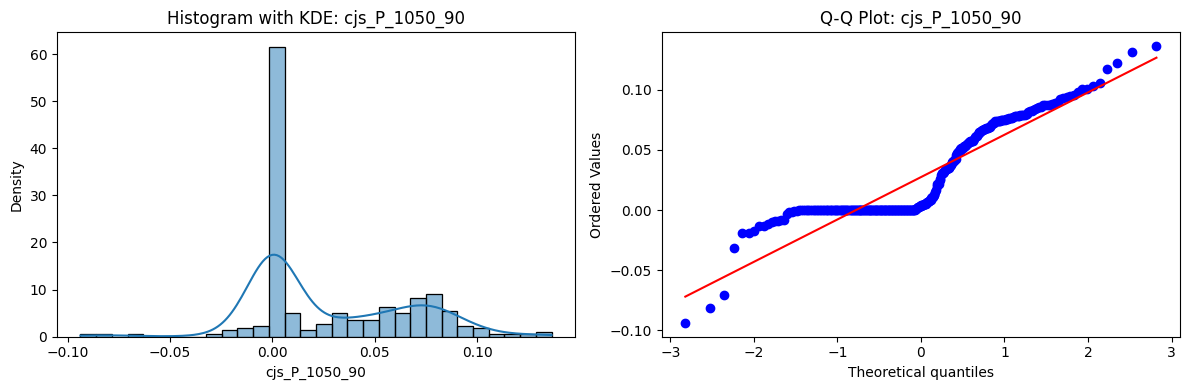
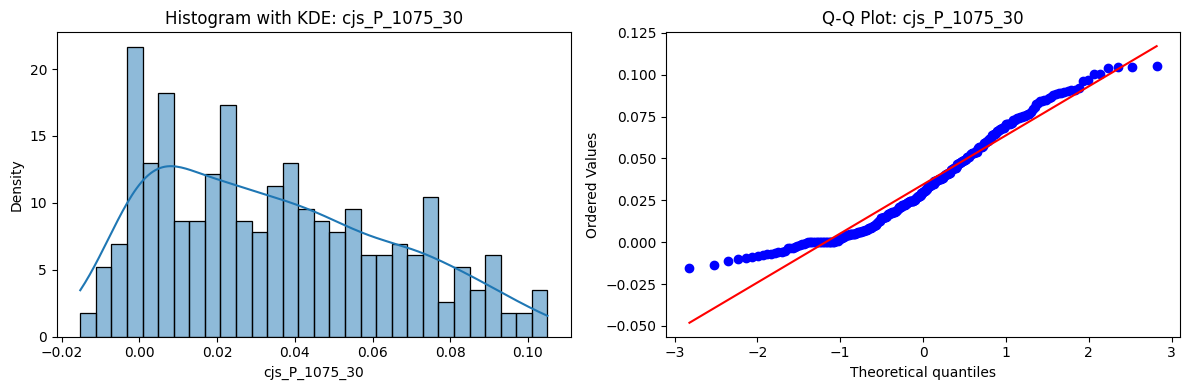
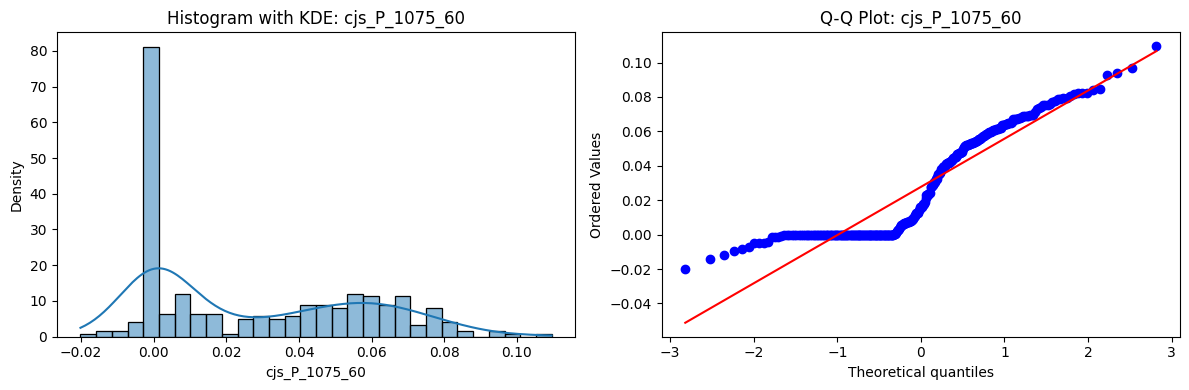
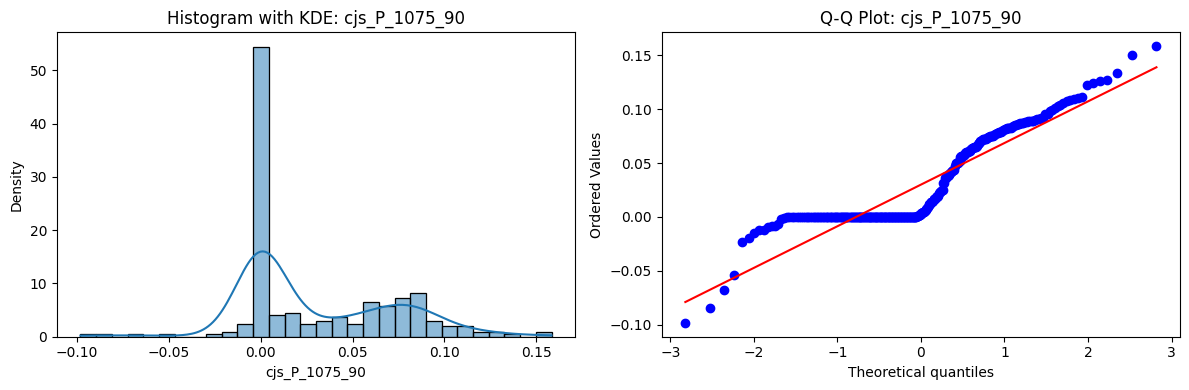
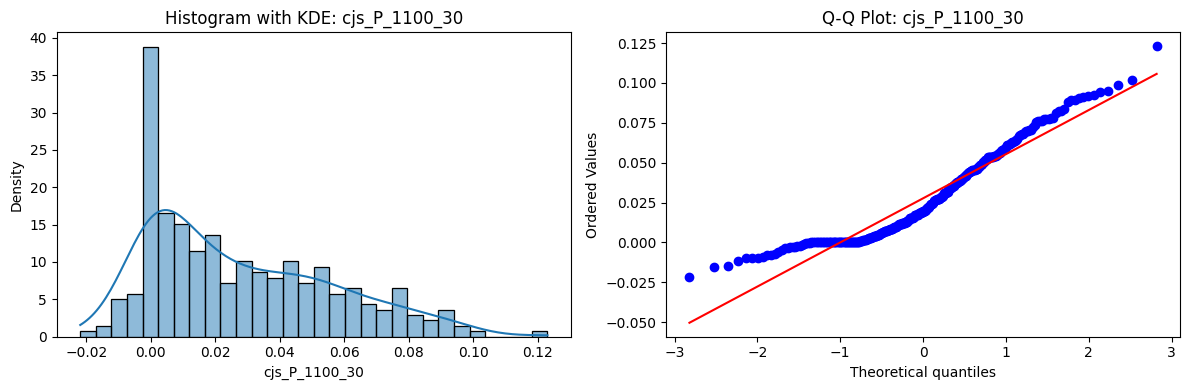
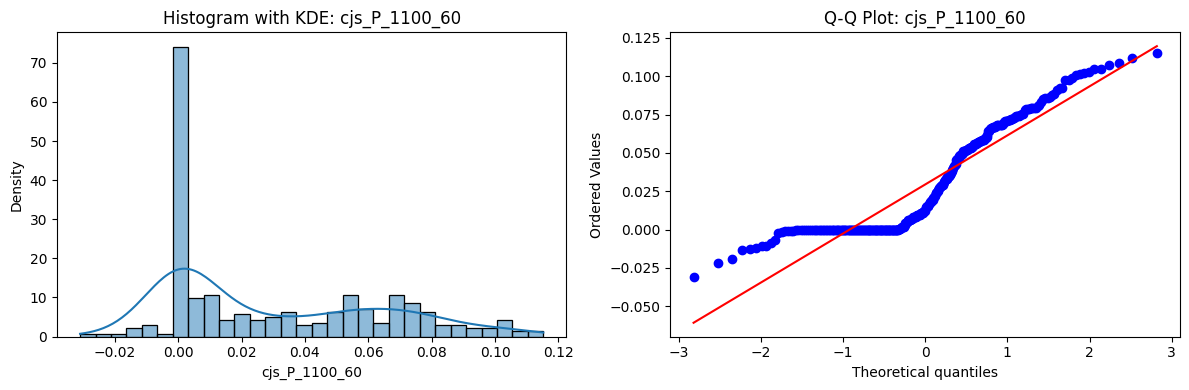
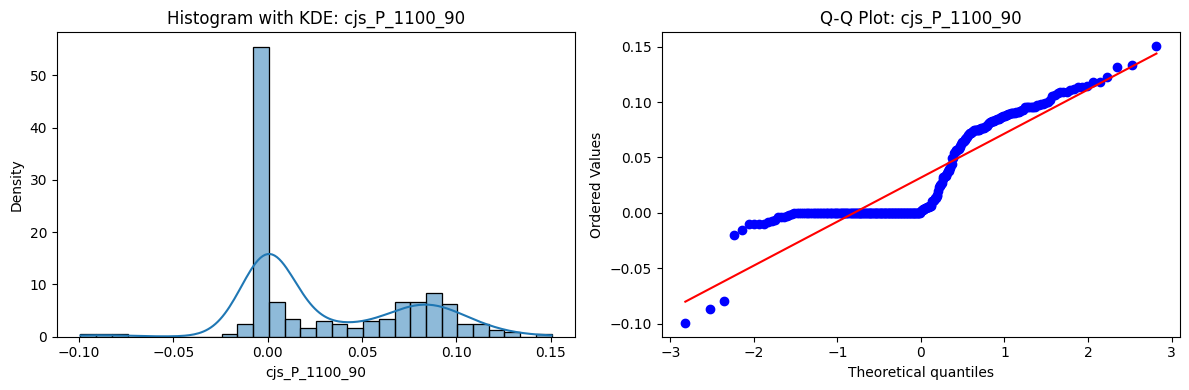
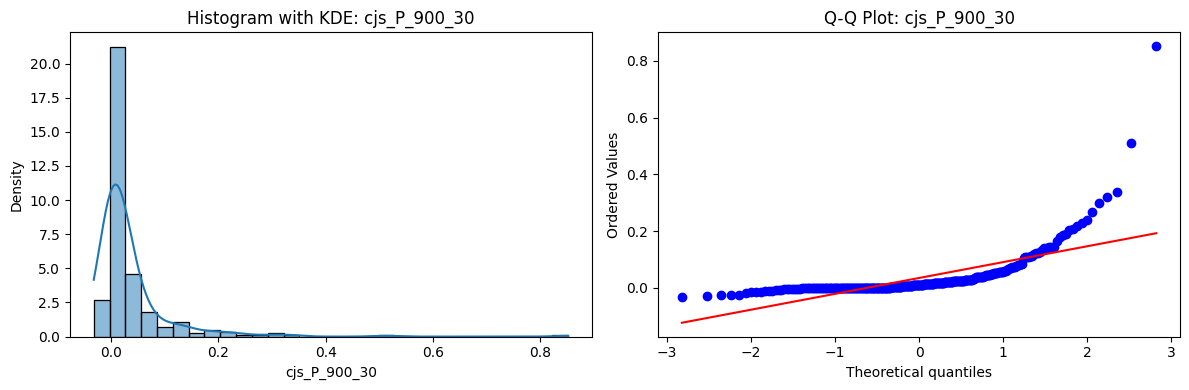
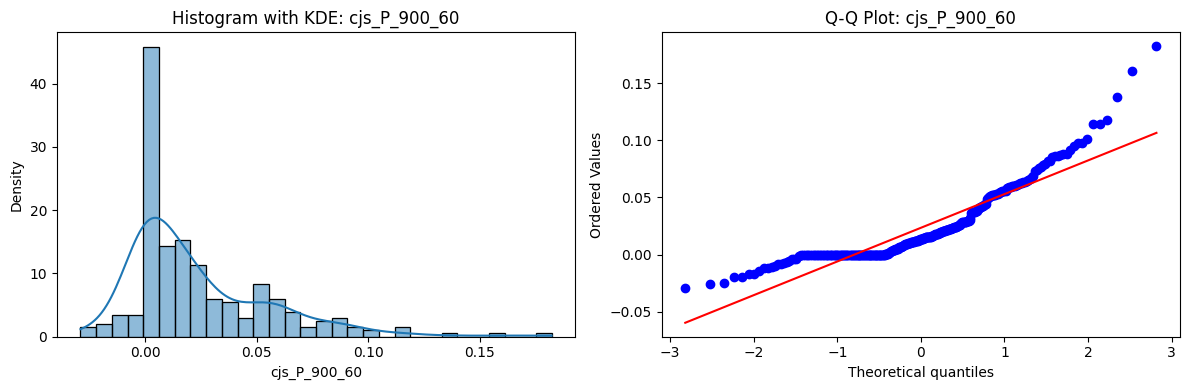
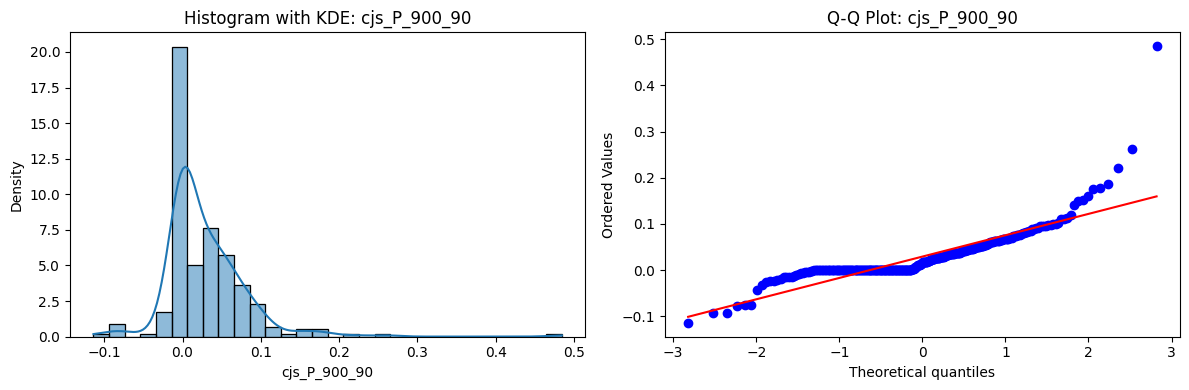
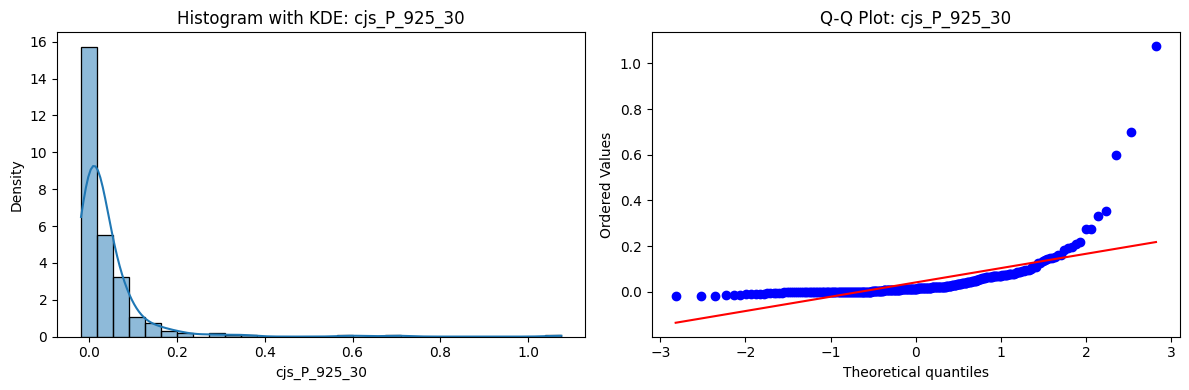
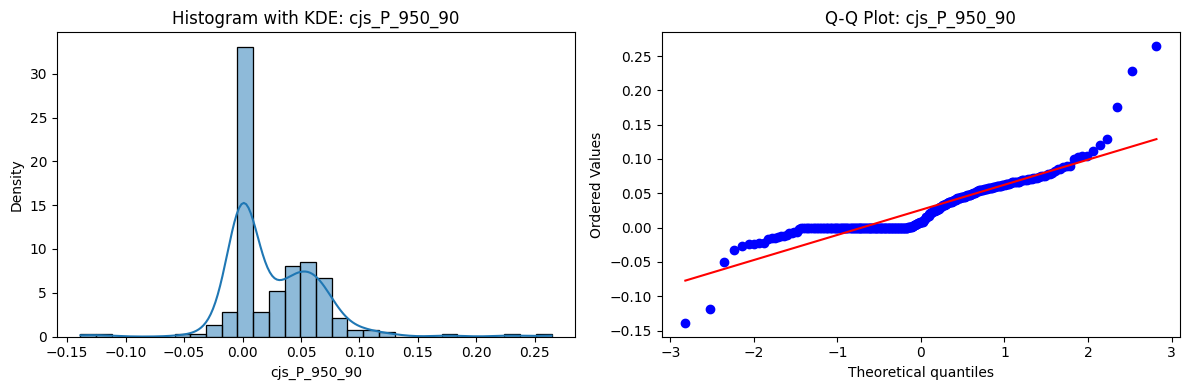
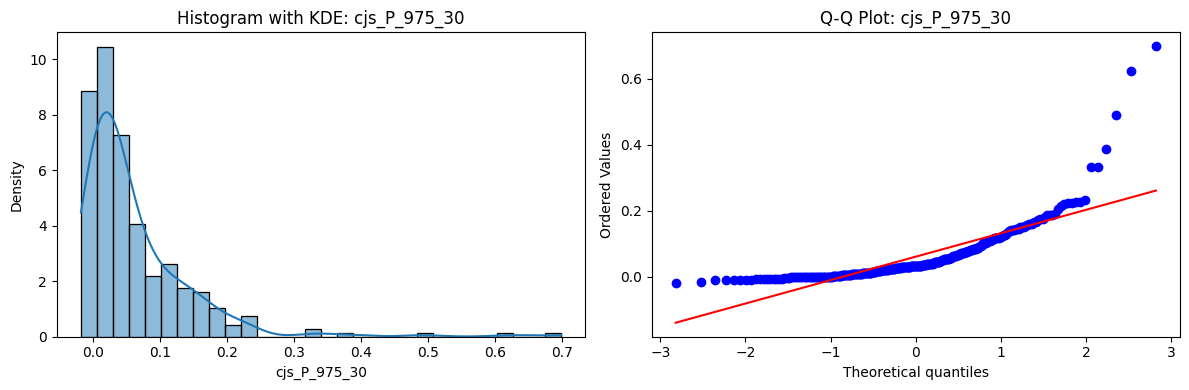
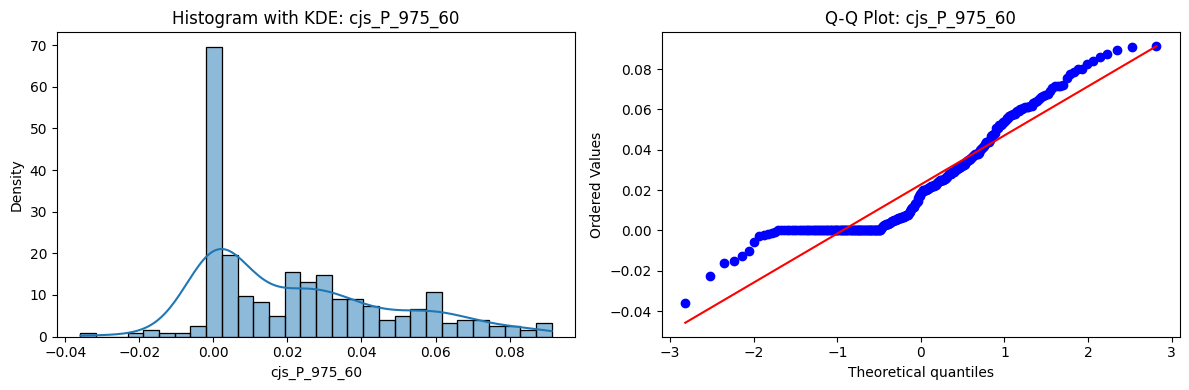
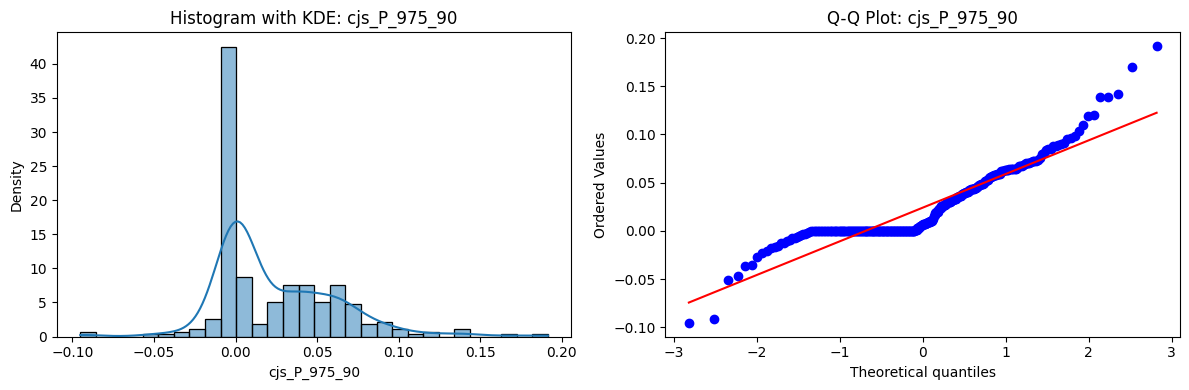
Distributions and Q-Q plots of the 54 CJS portfolios are shown below, based on the filtration and portfolio construction we have implemented.
Normality Tests (Shapiro, Jarque-Bera, Normaltest p-values): All means and medians ≈ 0, with maximums < 0.05. This indicates systematic rejection of normality at conventional significance levels (1% and 5%) for essentially all portfolios. In other words: none of these return distributions look Gaussian.
Skewness: Mean skewness ≈ 1.64, median ≈ 0.77 → distributions tend to be right-skewed (long right tails). Wide spread (std ≈ 2.26; max ≈ 11.1, min ≈ -0.91) → some portfolios are extremely positively skewed, while a few have mild negative skew.
Kurtosis: Mean kurtosis ≈ 14.5, median ≈ 4.6 (close to normal’s 3, but slightly higher). Very large spread (std ≈ 23.8; max ≈ 152.7) → many distributions are leptokurtic (fat-tailed). Averages are pulled up by extreme outliers, meaning some portfolios experience rare but massive return shocks.
returns_df = cjs_returns.copy()
returns_df = returns_df.reset_index().pivot_table(
columns="ftfsa_id", index="date", values="return"
)
# Apply to returns dataframe
summary_df = normality_summary(returns_df)
display(summary_df.describe().style.format(na_rep="NaN", precision=5, thousands=","))
# Plot histogram and QQ plot for each series
for col in returns_df.columns:
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 4))
sns.histplot(returns_df[col].dropna(), kde=True, stat="density", bins=30, ax=axs[0])
axs[0].set_title(f"Histogram with KDE: {col}")
stats.probplot(returns_df[col].dropna(), dist="norm", plot=axs[1])
axs[1].set_title(f"Q-Q Plot: {col}")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
| Shapiro_p | JarqueBera_p | Normaltest_p | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 54.00000 | 54.00000 | 54.00000 | 54.00000 | 54.00000 |
| mean | 0.00000 | 0.00228 | 0.00276 | 1.63759 | 14.52659 |
| std | 0.00000 | 0.00805 | 0.00801 | 2.25902 | 23.79816 |
| min | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | -0.90799 | 1.83906 |
| 25% | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.22364 | 2.98662 |
| 50% | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.77120 | 4.61425 |
| 75% | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00003 | 2.87608 | 18.37195 |
| max | 0.00000 | 0.04874 | 0.04428 | 11.10561 | 152.67355 |
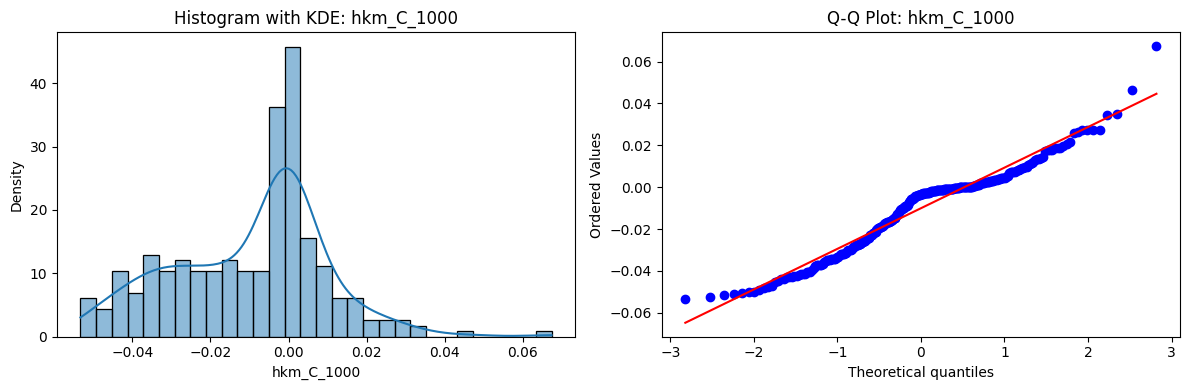
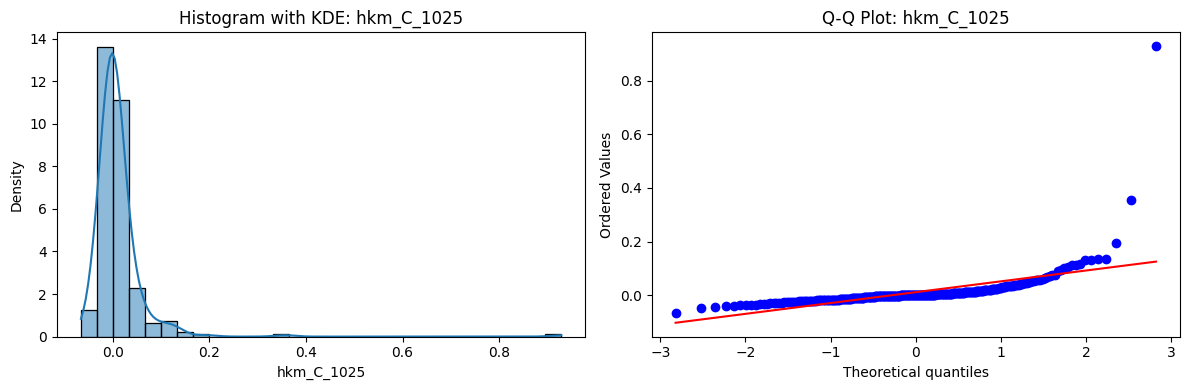
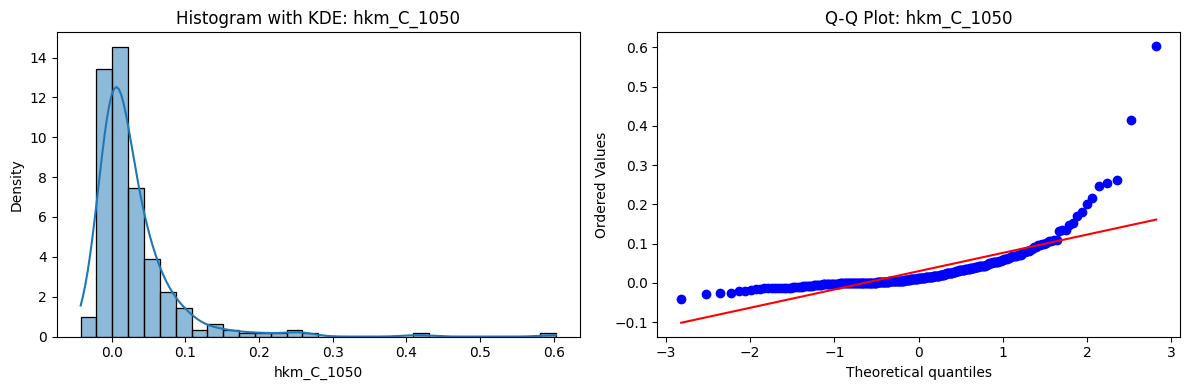
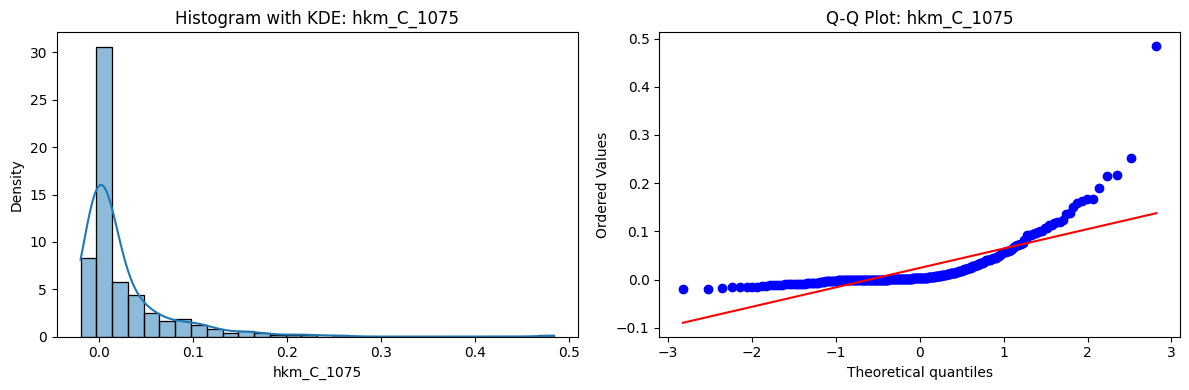
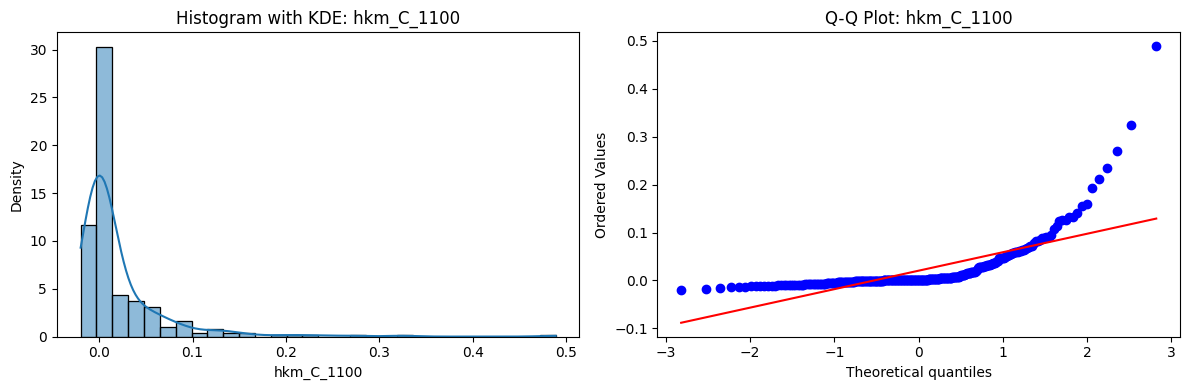
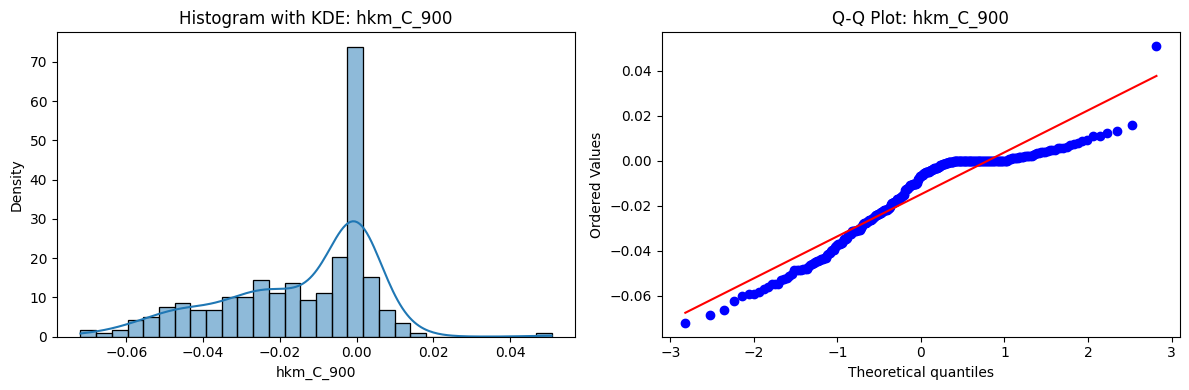
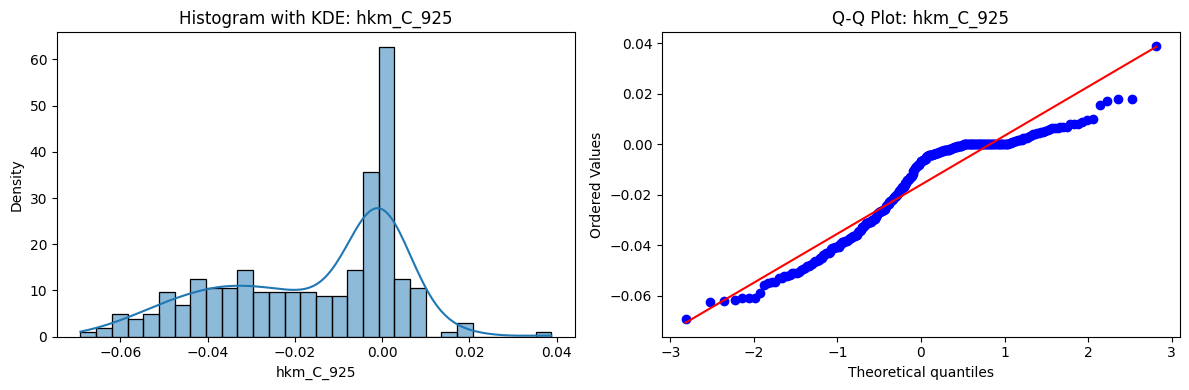
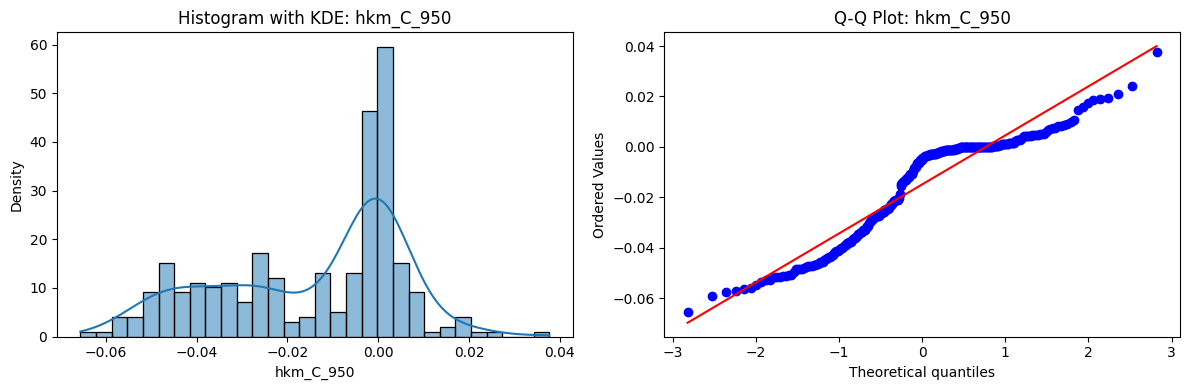
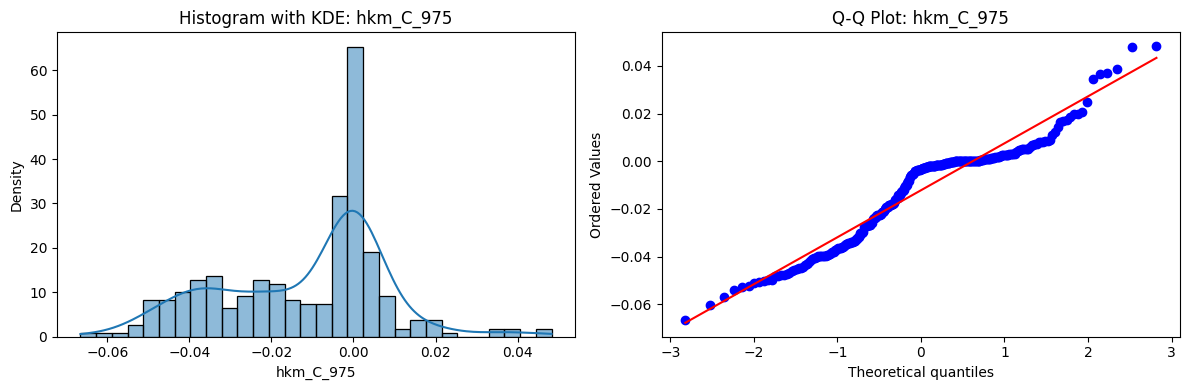
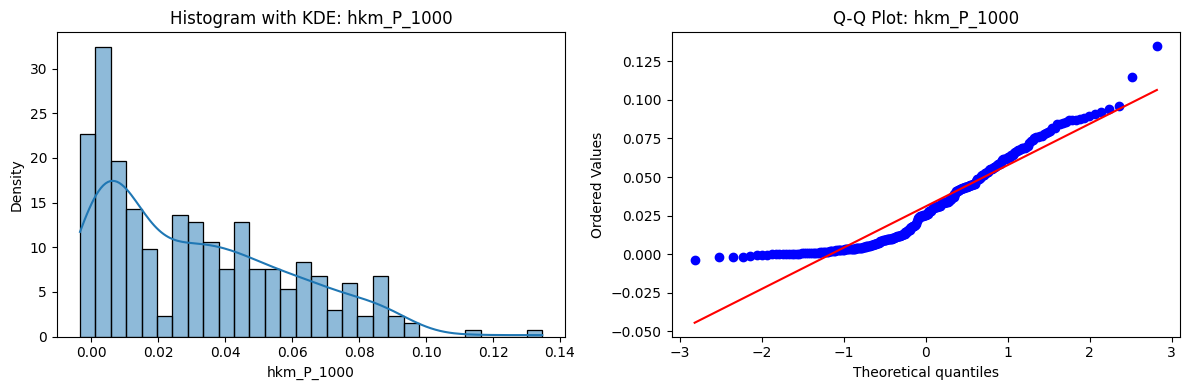
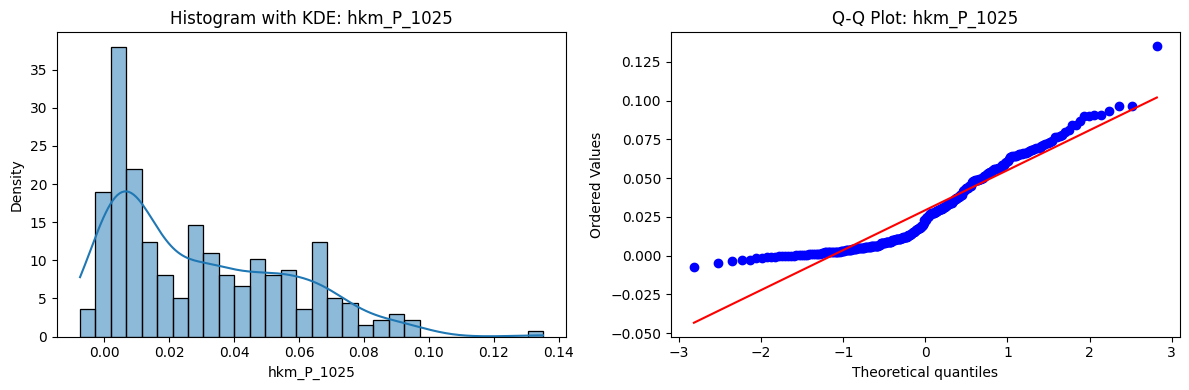
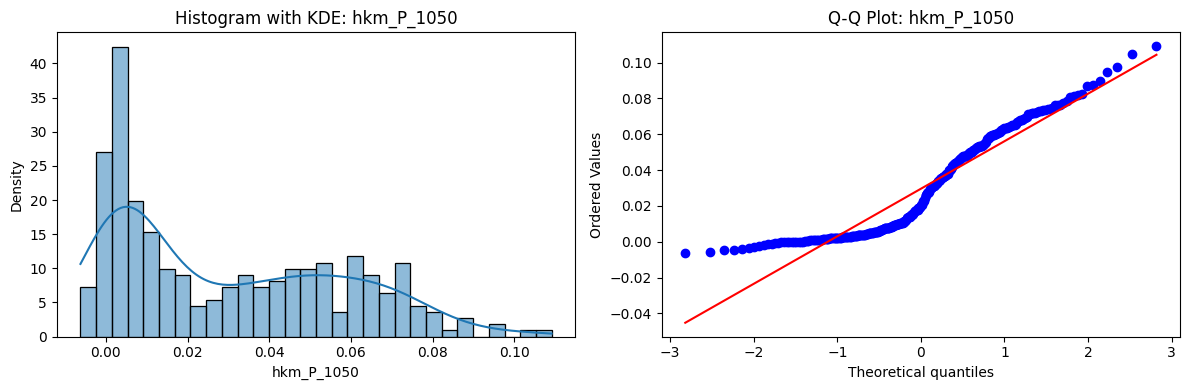
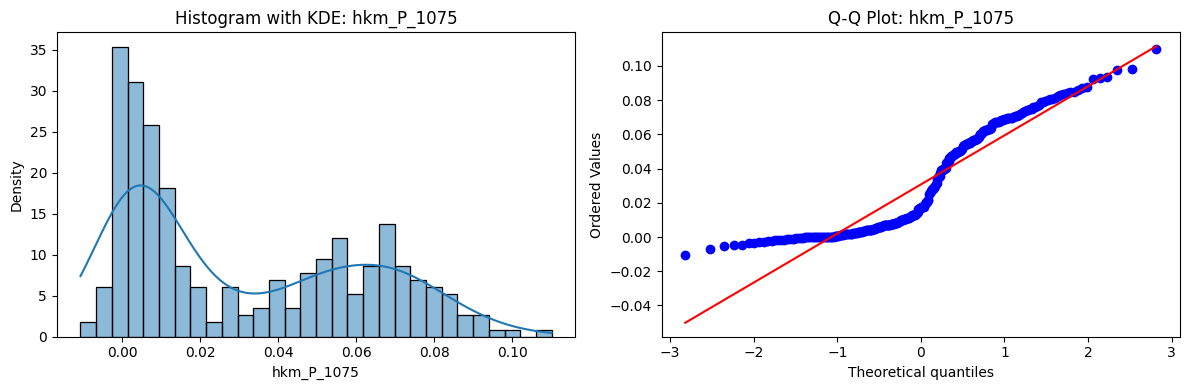
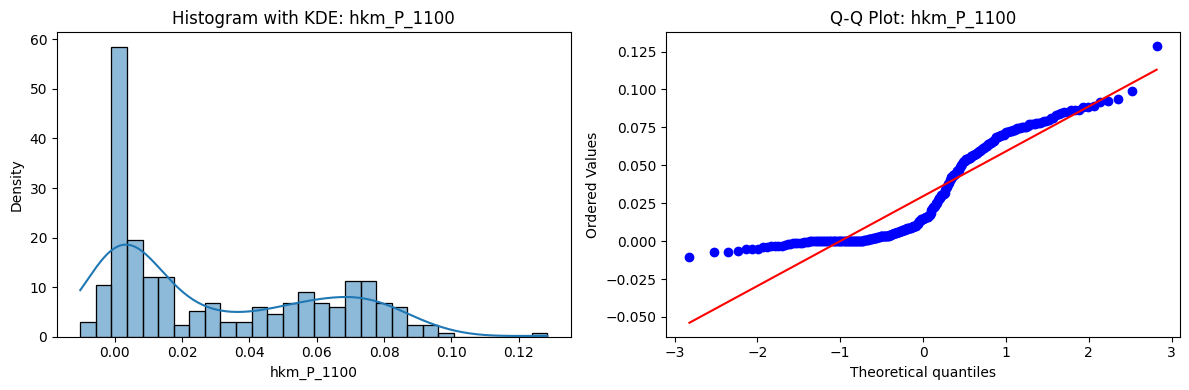
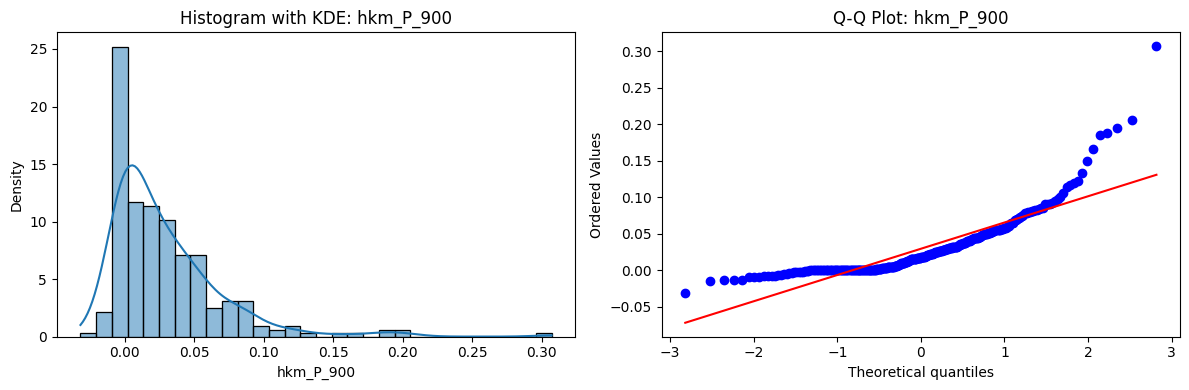
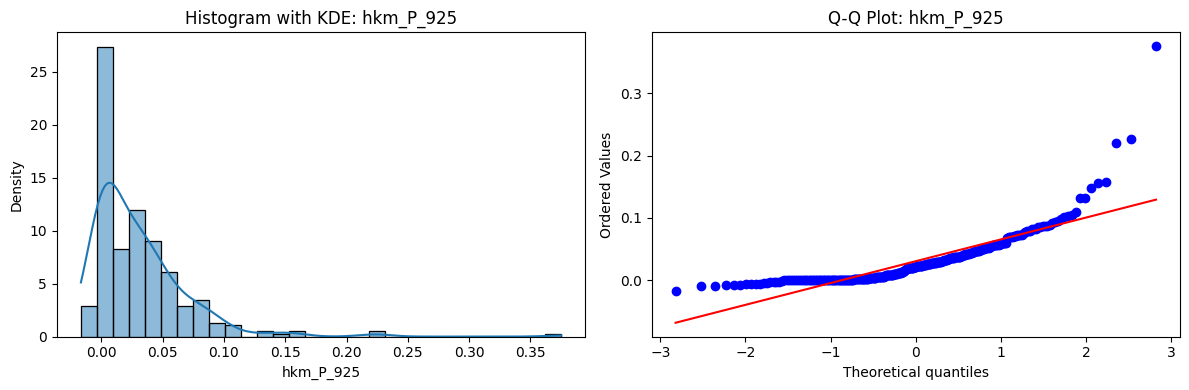
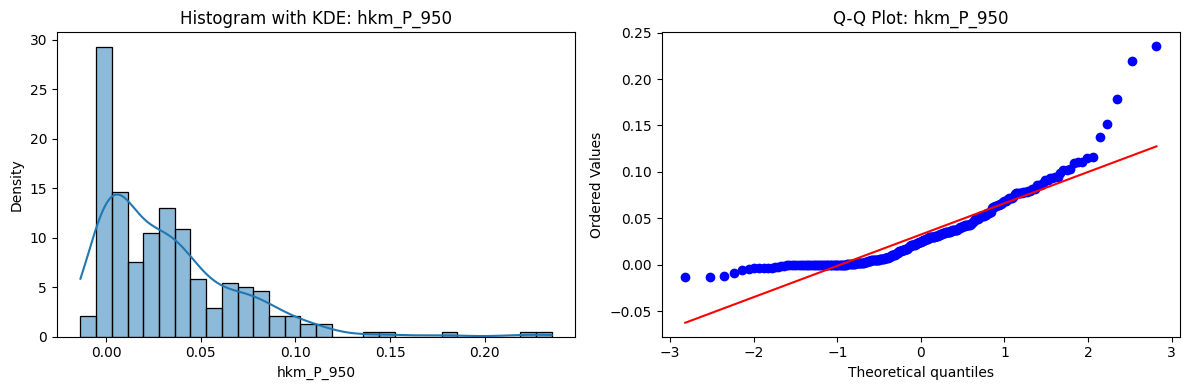
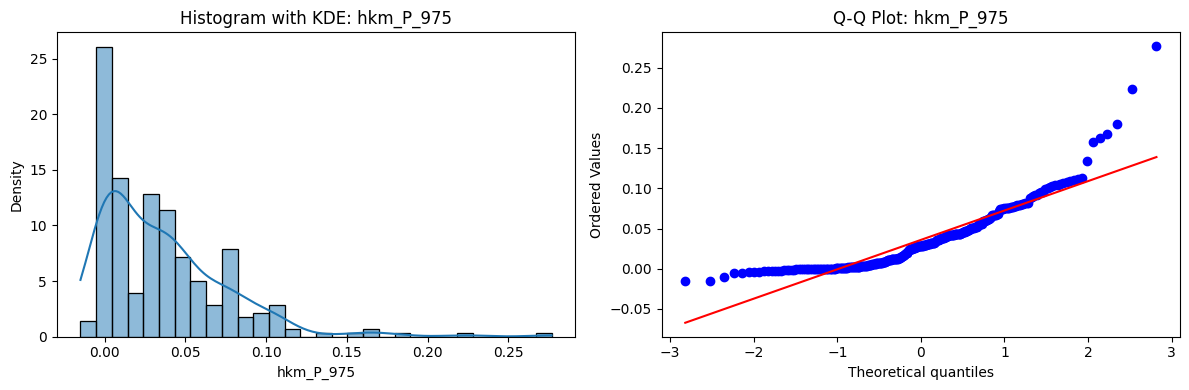
Tests for Normality of Returns in the 18 HKM Portfolios#
Distributions and Q-Q plots of the 18 HKM portfolios are shown below, based on the filtration and portfolio construction we have implemented.
Normality Tests:
Shapiro p-values: all 0 → normality always rejected.
Jarque-Bera & Normaltest p-values: means ~0.05, with maximums up to ~0.70 and ~0.61 respectively. Some portfolios do not reject normality at the 5% level, unlike the first dataset (where rejection was universal). Suggests a few return distributions here are closer to Gaussian, but the majority still deviate.
Skewness: Mean ≈ 1.87, median ≈ 0.78, similar to the first set (mean ≈ 1.64). Distribution wider: standard deviation ≈ 2.64, maximum ≈ 9.8. Takeaway: again, portfolios are generally positively skewed, with several highly right-tailed portfolios.
Kurtosis: Mean ≈ 16.8, median ≈ 3.1. This median is much closer to normal (3.0) than in the first dataset (median ≈ 4.6). Spread large (std ≈ 30.3, max ≈ 129.3) → still evidence of extreme fat tails in some cases, but fewer portfolios appear strongly leptokurtic compared to the first set. Comparison with the 54-Portfolios Set
returns_df = hkm_returns.copy()
returns_df = returns_df.reset_index().pivot_table(
columns="ftfsa_id", index="date", values="return"
)
# Apply to returns dataframe
summary_df = normality_summary(returns_df)
display(summary_df.describe().style.format(na_rep="NaN", precision=5, thousands=","))
# Plot histogram and QQ plot for each series
for col in returns_df.columns:
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 4))
sns.histplot(returns_df[col].dropna(), kde=True, stat="density", bins=30, ax=axs[0])
axs[0].set_title(f"Histogram with KDE: {col}")
stats.probplot(returns_df[col].dropna(), dist="norm", plot=axs[1])
axs[1].set_title(f"Q-Q Plot: {col}")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
| Shapiro_p | JarqueBera_p | Normaltest_p | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| count | 18.00000 | 18.00000 | 18.00000 | 18.00000 | 18.00000 |
| mean | 0.00000 | 0.05090 | 0.04631 | 1.86917 | 16.77614 |
| std | 0.00000 | 0.16958 | 0.15018 | 2.64475 | 30.26227 |
| min | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | -0.70095 | 1.84262 |
| 25% | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.08527 | 2.46929 |
| 50% | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.00000 | 0.77842 | 3.09835 |
| 75% | 0.00000 | 0.00001 | 0.00000 | 3.12405 | 20.20166 |
| max | 0.00000 | 0.69876 | 0.60995 | 9.83980 | 129.33881 |